Gene regulatory network of unfolded protein response genes in endoplasmic reticulum stress
- PMID: 22802018
- PMCID: PMC3508129
- DOI: 10.1007/s12192-012-0351-5
Gene regulatory network of unfolded protein response genes in endoplasmic reticulum stress
Abstract
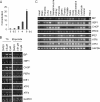
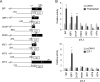
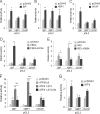
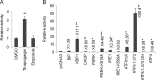
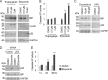
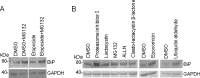
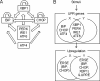
In the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), secretory and membrane proteins are properly folded and modified, and the failure of these processes leads to ER stress. At the same time, unfolded protein response (UPR) genes are activated to maintain homeostasis. Despite the thorough characterization of the individual gene regulation of UPR genes to date, further investigation of the mutual regulation among UPR genes is required to understand the complex mechanism underlying the ER stress response. In this study, we aimed to reveal a gene regulatory network formed by UPR genes, including immunoglobulin heavy chain-binding protein (BiP), X-box binding protein 1 (XBP1), C/EBP [CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein]-homologous protein (CHOP), PKR-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase (PERK), inositol-requiring 1 (IRE1), activating transcription factor 6 (ATF6), and ATF4. For this purpose, we focused on promoter-luciferase reporters for BiP, XBP1, and CHOP genes, which bear an ER stress response element (ERSE), and p5 × ATF6-GL3, which bears an unfolded protein response element (UPRE). We demonstrated that the luciferase activities of the BiP and CHOP promoters were upregulated by all the UPR genes, whereas those of the XBP1 promoter and p5 × ATF6-GL3 were upregulated by all the UPR genes except for BiP, CHOP, and ATF4 in HeLa cells. Therefore, an ERSE- and UPRE-centered gene regulatory network of UPR genes could be responsible for the robustness of the ER stress response. Finally, we revealed that BiP protein was degraded when cells were treated with DNA-damaging reagents, such as etoposide and doxorubicin; this finding suggests that the expression level of BiP is tightly regulated at the post-translational level, rather than at the transcriptional level, in the presence of DNA damage.
Figures

References
-
- Fawcett TW, Martindale JL, Guyton KZ, Hai T, Holbrook NJ. Complexes containing activating transcription factor (ATF)/cAMP-responsive-element-binding protein (CREB) interact with the CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein (C/EBP)-ATF composite site to regulate Gadd153 expression during the stress response. Biochem J. 1999;339:135–141. doi: 10.1042/0264-6021:3390135. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hetz C. The unfolded protein response: controlling cell fate decisions under ER stress and beyond. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012;13:89–102. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

