Pyk2 cytonuclear localization: mechanisms and regulation by serine dephosphorylation
- PMID: 22802128
- PMCID: PMC11113809
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-012-1075-5
Pyk2 cytonuclear localization: mechanisms and regulation by serine dephosphorylation
Abstract
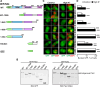
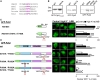
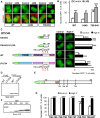
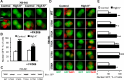
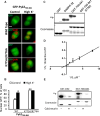
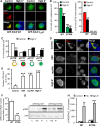
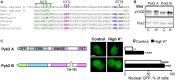
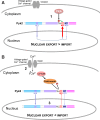
Cytonuclear signaling is essential for long-term alterations of cellular properties. Several pathways involving regulated nuclear accumulation of Ser/Thr kinases have been described but little is known about cytonuclear trafficking of tyrosine kinases. Proline-rich tyrosine kinase 2 (Pyk2) is a cytoplasmic non-receptor tyrosine kinase enriched in neurons and involved in functions ranging from synaptic plasticity to bone resorption, as well as in cancer. We previously showed the Ca(2+)-induced, calcineurin-dependent, nuclear localization of Pyk2. Here, we characterize the molecular mechanisms of Pyk2 cytonuclear localization in transfected PC12 cells. The 700-841 linker region of Pyk2 recapitulates its depolarization-induced nuclear accumulation. This region includes a nuclear export motif regulated by phosphorylation at residue S778, a substrate of cAMP-dependent protein kinase and calcineurin. Nuclear import is controlled by a previously identified sequence in the N-terminal domain and by a novel nuclear targeting signal in the linker region. Regulation of cytonuclear trafficking is independent of Pyk2 activity. The region regulating nuclear localization is absent from the non-neuronal shorter splice isoform of Pyk2. Our results elucidate the mechanisms of Ca(2+)-induced nuclear accumulation of Pyk2. They also suggest that Pyk2 nuclear accumulation is a novel type of signaling response that may contribute to specific long-term adaptations in neurons.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

