Role of heme oxygenase-1 in polymyxin B-induced nephrotoxicity in rats
- PMID: 22802257
- PMCID: PMC3457368
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00925-12
Role of heme oxygenase-1 in polymyxin B-induced nephrotoxicity in rats
Abstract
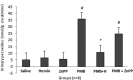
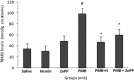
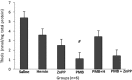
Polymyxin B (PMB) is a cationic polypeptide antibiotic with activity against multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria. PMB-induced nephrotoxicity consists of direct toxicity to the renal tubules and the release of reactive oxygen species (ROS) with oxidative damage. This study evaluated the nephroprotective effect of heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) against PMB-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Adult male Wistar rats, weighing 286 ± 12 g, were treated intraperitoneally once a day for 5 days with saline, hemin (HO-1 inducer; 10 mg/kg), zinc protoporphyrin (ZnPP) (HO-1 inhibitor; 50 μmol/kg, administered before PMB on day 5), PMB (4 mg/kg), PMB plus hemin, and PMB plus ZnPP. Renal function (creatinine clearance, Jaffe method), urinary peroxides (ferrous oxidation of xylenol orange version 2 [FOX-2]), urinary thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances (TBARS), renal tissue thiols, catalase activity, and renal tissue histology were analyzed. The results showed that PMB reduced creatinine clearance (P < 0.05), with an increase in urinary peroxides and TBARS. The PMB toxicity caused a reduction in catalase activity and thiols (P < 0.05). Hemin attenuated PMB nephrotoxicity by increasing the catalase antioxidant activity (P < 0.05). The combination of PMB and ZnPP incremented the fractional interstitial area of renal tissue (P < 0.05), and acute tubular necrosis in the cortex area was also observed. This is the first study demonstrating the protective effect of HO-1 against PMB-induced nephrotoxicity.
Figures


References
-
- Aebi H. 1984. Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol. 105:121–126 - PubMed
-
- Agarwal A, Balla J, Alam J, Croatt AJ, Nath KA. 1995. Induction of heme oxygenase in toxic renal injury: a protective role in cisplatin nephrotoxicity in the rat. Kidney Int. 48:1298–1307 - PubMed
-
- Agarwal A, Nick HS. 2000. Renal response to tissue injury: lessons from heme oxygenase-1 gene ablation and expression. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 11:965–973 - PubMed
-
- Akerboom TPM, Sies H. 1981. Assay glutathione, glutathione disulfide, and glutathione mixed disulfides in biological samples. Methods Enzymol. 77:373–382 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

