Insights into Lantibiotic Immunity Provided by Bioengineering of LtnI
- PMID: 22802258
- PMCID: PMC3457384
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00979-12
Insights into Lantibiotic Immunity Provided by Bioengineering of LtnI
Abstract
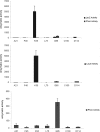
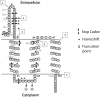
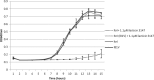
The lantibiotic lacticin 3147 has been the focus of much research due to its broad spectrum of activity against many microbial targets, including drug-resistant pathogens. In order to protect itself, a lacticin 3147 producer must possess a cognate immunity mechanism. Lacticin 3147 immunity is provided by an ABC transporter, LtnFE, and a dedicated immunity protein, LtnI, both of which are capable of independently providing a degree of protection. In the study described here, we carried out an in-depth investigation of LtnI structure-function relationships through the creation of a series of fusion proteins and LtnI determinants that have been the subject of random and site-directed mutagenesis. We establish that LtnI is a transmembrane protein that contains a number of individual residues and regions, such as those between amino acids 20 and 27 and amino acids 76 and 83, which are essential for LtnI function. Finally, as a consequence of the screening of a bank of 28,000 strains producing different LtnI derivatives, we identified one variant (LtnI I81V) that provides enhanced protection. To our knowledge, this is the first report of a lantibiotic immunity protein with enhanced functionality.
Figures


References
-
- Aso Y, et al. 2005. A novel type of immunity protein, NukH, for the lantibiotic nukacin ISK-1 produced by Staphylococcus warneri ISK-1. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 69:1403–1410 - PubMed
-
- Breukink E, de Kruijff B. 2006. Lipid II as a target for antibiotics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 5:321–332 - PubMed
-
- Brumfitt W, Salton MR, Hamilton-Miller JM. 2002. Nisin, alone and combined with peptidoglycan-modulating antibiotics: activity against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and vancomycin-resistant enterococci. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 50:731–734 - PubMed
-
- Chatterjee C, Paul M, Xie L, van der Donk WA. 2005. Biosynthesis and mode of action of lantibiotics. Chem. Rev. 105:633–684 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

