Patterns of survival among patients with myeloproliferative neoplasms diagnosed in Sweden from 1973 to 2008: a population-based study
- PMID: 22802311
- PMCID: PMC3417050
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2012.42.1925
Patterns of survival among patients with myeloproliferative neoplasms diagnosed in Sweden from 1973 to 2008: a population-based study
Abstract
Purpose: Reported survival in patients with myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs) shows great variation. Patients with primary myelofibrosis (PMF) have substantially reduced life expectancy, whereas patients with polycythemia vera (PV) and essential thrombocythemia (ET) have moderately reduced survival in most, but not all, studies. We conducted a large population-based study to establish patterns of survival in more than 9,000 patients with MPNs.
Patients and methods: We identified 9,384 patients with MPNs (from the Swedish Cancer Register) diagnosed from 1973 to 2008 (divided into four calendar periods) with follow-up to 2009. Relative survival ratios (RSRs) and excess mortality rate ratios were computed as measures of survival.
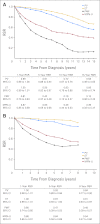
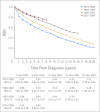
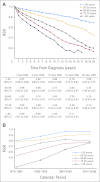
Results: Patient survival was considerably lower in all MPN subtypes compared with expected survival in the general population, reflected in 10-year RSRs of 0.64 (95% CI, 0.62 to 0.67) in patients with PV, 0.68 (95% CI, 0.64 to 0.71) in those with ET, and 0.21 (95% CI, 0.18 to 0.25) in those with PMF. Excess mortality was observed in patients with any MPN subtype during all four calendar periods (P < .001). Survival improved significantly over time (P < .001); however, the improvement was less pronounced after the year 2000 and was confined to patients with PV and ET.
Conclusion: We found patients with any MPN subtype to have significantly reduced life expectancy compared with the general population. The improvement over time is most likely explained by better overall clinical management of patients with MPN. The decreased life expectancy even in the most recent calendar period emphasizes the need for new treatment options for these patients.
Figures

References
-
- Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, et al. Lyon, France: IARC Press; 2008. WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues.
-
- Kralovics R, Passamonti F, Buser AS, et al. A gain-of-function mutation of JAK2 in myeloproliferative disorders. N Engl J Med. 2005;352:1779–1790. - PubMed
-
- Levine RL, Wadleigh M, Cools J, et al. Activating mutation in the tyrosine kinase JAK2 in polycythemia vera, essential thrombocythemia, and myeloid metaplasia with myelofibrosis. Cancer Cell. 2005;7:387–397. - PubMed
-
- James C, Ugo V, Le Couédic JP, et al. A unique clonal JAK2 mutation leading to constitutive signalling causes polycythaemia vera. Nature. 2005;434:1144–1148. - PubMed
-
- Baxter EJ, Scott LM, Campbell PJ, et al. Acquired mutation of the tyrosine kinase JAK2 in human myeloproliferative disorders. Lancet. 2005;365:1054–1061. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

