Unexpected role for MHC II-peptide complexes in shaping CD8 T-cell expansion and differentiation in vivo
- PMID: 22802622
- PMCID: PMC3411949
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1207219109
Unexpected role for MHC II-peptide complexes in shaping CD8 T-cell expansion and differentiation in vivo
Abstract
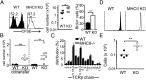
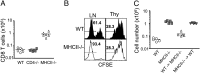
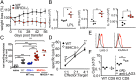
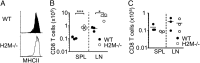
Here we report a unique role for MHC II-peptide complexes in controlling immune responses of naïve CD8 T cells. Compared with CD8 T cells from WT mice, CD8 T cells isolated from MHC II(-/-) mice hyperproliferated under lymphopenic conditions, differentiated into effector cells producing proinflammatory cytokines, and mediated more severe tissue inflammation. The elevated responses of MHC II(-/-) CD8 T cells were due to the absence of MHC II, but not CD4, T cells. The hyperreactivity appeared to be a feature of mature T cells, given its absence in CD8 single positive thymocytes derived from MHC II(-/-) mice. Expression of the MHC II ligand LAG3 was markedly enhanced during in vivo activation of MHC II(-/-) CD8 T cells, and blockade of MHC II-LAG3 interactions further enhanced T-cell expansion. Importantly, CD8 T cells isolated from H-2M(-/-) mice expressing WT levels of MHC II also displayed hyperresponsiveness similar to that of MHC II(-/-) CD8 T cells, suggesting that peptides presented on MHC II are involved in the control of CD8 T-cell responses. Our results uncover a previously undefined MHC II-dependent regulation that tunes CD8 T-cell reactivity and may have implications for an improved understanding of CD8 T-cell homeostasis and functions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Murali-Krishna K, et al. Persistence of memory CD8 T cells in MHC class I-deficient mice. Science. 1999;286:1377–1381. - PubMed
-
- Tanchot C, Lemonnier FA, Pérarnau B, Freitas AA, Rocha B. Differential requirements for survival and proliferation of CD8 naïve or memory T cells. Science. 1997;276:2057–2062. - PubMed
-
- Swain SL, Hu H, Huston G. Class II-independent generation of CD4 memory T cells from effectors. Science. 1999;286:1381–1383. - PubMed
-
- Dorfman JR, Stefanová I, Yasutomo K, Germain RN. CD4+ T cell survival is not directly linked to self-MHC–induced TCR signaling. Nat Immunol. 2000;1:329–335. - PubMed
-
- Clarke SR, Rudensky AY. Survival and homeostatic proliferation of naive peripheral CD4+ T cells in the absence of self-peptide:MHC complexes. J Immunol. 2000;165:2458–2464. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

