Transcriptional consequences of aneuploidy
- PMID: 22802626
- PMCID: PMC3411958
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1209227109
Transcriptional consequences of aneuploidy
Abstract
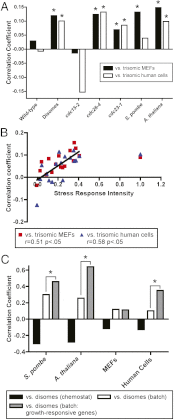
Aneuploidy, or an aberrant karyotype, results in developmental disabilities and has been implicated in tumorigenesis. However, the causes of aneuploidy-induced phenotypes and the consequences of aneuploidy on cell physiology remain poorly understood. We have performed a metaanalysis on gene expression data from aneuploid cells in diverse organisms, including yeast, plants, mice, and humans. We found highly related gene expression patterns that are conserved between species: genes that were involved in the response to stress were consistently upregulated, and genes associated with the cell cycle and cell proliferation were downregulated in aneuploid cells. Within species, different aneuploidies induced similar changes in gene expression, independent of the specific chromosomal aberrations. Taken together, our results demonstrate that aneuploidies of different chromosomes and in different organisms impact similar cellular pathways and cause a stereotypical antiproliferative response that must be overcome before transformation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Musacchio A, Salmon ED. The spindle-assembly checkpoint in space and time. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:379–393. - PubMed
-
- Weaver BA, Cleveland DW. Does aneuploidy cause cancer? Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2006;18:658–667. - PubMed
-
- Hassold T, et al. Human aneuploidy: Incidence, origin, and etiology. Environ Mol Mutagen. 1996;28:167–175. - PubMed
-
- Brown S. Miscarriage and its associations. Semin Reprod Med. 2008;26:391–400. - PubMed
-
- Delabar JM, et al. Molecular mapping of twenty-four features of Down syndrome on chromosome 21. Eur J Hum Genet. 1993;1:114–124. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

