p53 is an important regulator of CCL2 gene expression
- PMID: 22804246
- PMCID: PMC3786129
- DOI: 10.2174/156652412802480844
p53 is an important regulator of CCL2 gene expression
Abstract
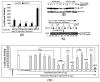
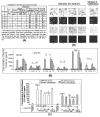
The p53 protein is a sequence-specific DNA-binding factor that regulates inflammatory genes such as CCL2/MCP-1 that may play a role in various diseases. A recent study has indicated that the knockdown of human p53 leads to a strong negative regulation of CCL2 induction. We are therefore interested in how p53 regulates CCL2 gene expression. In the following study, our findings indicate that UV-induced p53 accumulation in mouse macrophages significantly decreases LPS-induced CCL2 production, and that p53 binds to CCL2 5'UTR in the region (16-35). We also found that a p53 domain (p53pep170) mimics full length p53 to down-regulate CCL2 promoter activity. Treatment of p53-deficient mouse primary macrophages with synthetic p53pep170 was found to decrease LPS-induced production of CCL2 without association with cellular endogenous p53. CCL2 production induced by lentiCLG in human monocytes or mouse primary macrophages was blocked in the presence of p53pep170. Overall, these results demonstrate that p53 or its derived peptide (p53pep170) is an important regulator of CCL2 gene expression via its binding activity, and acts as a novel model for future studies linking p53 and its short peptide to pave the way to possible pharmaceutical intervention of CCL2-mediated inflammatory and cancer diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors confirm that this article content has no conflicts of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
p53 suppresses CCL2-induced subcutaneous tumor xenograft.Tumour Biol. 2015 Apr;36(4):2801-8. doi: 10.1007/s13277-014-2906-9. Epub 2014 Dec 11. Tumour Biol. 2015. PMID: 25492482 Free PMC article.
-
A circadian clock gene, Rev-erbα, modulates the inflammatory function of macrophages through the negative regulation of Ccl2 expression.J Immunol. 2014 Jan 1;192(1):407-17. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1301982. Epub 2013 Dec 4. J Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24307731
-
p53 peptide prevents LITAF-induced TNF-alpha-mediated mouse lung lesions and endotoxic shock.Curr Mol Med. 2011 Aug;11(6):439-52. doi: 10.2174/156652411796268731. Curr Mol Med. 2011. PMID: 21663590
-
Identification and characterization of the IKKalpha promoter: positive and negative regulation by ETS-1 and p53, respectively.J Biol Chem. 2004 Dec 10;279(50):52141-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M407915200. Epub 2004 Oct 5. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15469934
-
p53 short peptide (p53pep164) regulates lipopolysaccharide-induced tumor necrosis factor-alpha factor/cytokine expression.Cancer Res. 2007 Feb 1;67(3):1308-16. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-1600. Cancer Res. 2007. PMID: 17283168
Cited by
-
Immune surveillance of unhealthy cells by natural killer cells.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2013;78:249-57. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2013.78.020255. Epub 2013 Oct 17. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2013. PMID: 24135717 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oral bacteria and cancer.PLoS Pathog. 2014 Mar 27;10(3):e1003933. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003933. eCollection 2014 Mar. PLoS Pathog. 2014. PMID: 24676390 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Deficiency of miR-208a Exacerbates CCl4-Induced Acute Liver Injury in Mice by Activating Cell Death Pathways.Hepatol Commun. 2020 Aug 19;4(10):1487-1501. doi: 10.1002/hep4.1540. eCollection 2020 Oct. Hepatol Commun. 2020. PMID: 33024918 Free PMC article.
-
The role of p53 in anti-tumor immunity and response to immunotherapy.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Aug 1;10:1148389. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1148389. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 37602328 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of environmental chemicals that enable the cancer hallmark of evasion of growth suppression.Carcinogenesis. 2015 Jun;36 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S2-18. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgv028. Carcinogenesis. 2015. PMID: 26106139 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rohaly G, Chemnitz J, Dehde S, et al. A novel human p53 isoform is an essential element of the ATR-intra-S phase checkpoint. Cell. 2005;122:21–32. - PubMed
-
- Virginie M, Staphane P, Mustapha A, et al. Delta160p53 is a novel N-terminal p53 isoform encoded by delta133p53 transcript. FEBS Lett. 2010;584:4463–8. - PubMed
-
- Avery-Kiejda KA, Zhang XD, Adams LJ, et al. Small molecular weight variants of p53 are expressed in human melanoma cells and are induced by the DNA-damaging agent cisplatin. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14:1659–68. - PubMed
-
- Hofstetter G, Berger A, Fiegl H, et al. Aoternative splicing of p53 and p73: the novel p53 splice variant p53 delta is an independent prognostic marker in ovarian cancer. Oncogene. 2010;29:1997–2004. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
