Voluntary wheel running selectively augments insulin-stimulated vasodilation in arterioles from white skeletal muscle of insulin-resistant rats
- PMID: 22804760
- PMCID: PMC3498513
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1549-8719.2012.00210.x
Voluntary wheel running selectively augments insulin-stimulated vasodilation in arterioles from white skeletal muscle of insulin-resistant rats
Abstract
Background: Exercise (RUN) prevents declines in insulin-mediated vasodilation, an important component of insulin-mediated glucose disposal, in rats prone to obesity and insulin resistance.
Objective: Determine whether RUN (1) improves insulin-stimulated vasodilation after insulin resistance has been established, and (2) differentially affects arterioles from red and white muscle.
Methods: Insulin signaling and vasoreactivity to insulin (1-1000 μIU/mL) were assessed in 2A from the Gw and Gr of SED OLETF rats at 12 and 20 weeks of age (SED12, SED20) and those undergoing RUN (RUN20) or caloric restriction (CR20; to match body weight of RUN) from 12 to 20 weeks.
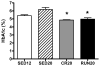
Results: Glucose and insulin responses to i.p. glucose were reduced in RUN20, elevated in SED20 (p < 0.05 vs. SED12), and maintained in CR20. Insulin-stimulated vasodilation was greater in Gw but not Gr, 2As of RUN20 (p < 0.01 vs. all groups), and was improved by ET-1 receptor inhibition in Gw 2As from SED20 and CR20 (p < 0.05). There were no differences in microvascular insulin signaling among groups or muscle beds.
Conclusions: RUN selectively improved insulin-mediated vasodilation in Gw 2As, in part through attenuated ET-1 sensitivity/production, an adaptation that was independent of changes in adiposity and may contribute to enhanced insulin-stimulated glucose disposal.
© 2012 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Daily physical activity enhances reactivity to insulin in skeletal muscle arterioles of hyperphagic Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima Fatty rats.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2010 Oct;109(4):1203-10. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00064.2010. Epub 2010 Jul 15. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2010. PMID: 20634354 Free PMC article.
-
Functional adaptations in the skeletal muscle microvasculature to endurance and interval sprint training in the type 2 diabetic OLETF rat.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2012 Oct 15;113(8):1223-32. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00823.2012. Epub 2012 Aug 23. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2012. PMID: 22923508 Free PMC article.
-
A chronic physical activity treatment in obese rats normalizes the contributions of ET-1 and NO to insulin-mediated posterior cerebral artery vasodilation.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2017 Apr 1;122(4):1040-1050. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00811.2016. Epub 2017 Feb 9. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2017. PMID: 28183819 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolism and insulin signaling in common metabolic disorders and inherited insulin resistance.Dan Med J. 2014 Jul;61(7):B4890. Dan Med J. 2014. PMID: 25123125 Review.
-
Insulin-stimulated glucose uptake in healthy and insulin-resistant skeletal muscle.Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig. 2016 Apr 1;26(1):13-24. doi: 10.1515/hmbci-2015-0041. Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig. 2016. PMID: 26485752 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of habitual physical activity in modulating vascular actions of insulin.Exp Physiol. 2015 Jul 1;100(7):759-71. doi: 10.1113/EP085107. Exp Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26130183 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Divergent role of nitric oxide in insulin-stimulated aortic vasorelaxation between low- and high-intrinsic aerobic capacity rats.Physiol Rep. 2015 Jul;3(7):e12459. doi: 10.14814/phy2.12459. Physiol Rep. 2015. PMID: 26197933 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise-induced differential changes in gene expression among arterioles of skeletal muscles of obese rats.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2015 Sep 15;119(6):583-603. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00316.2015. Epub 2015 Jul 16. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2015. PMID: 26183477 Free PMC article.
-
Endurance, interval sprint, and resistance exercise training: impact on microvascular dysfunction in type 2 diabetes.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2016 Feb 1;310(3):H337-50. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00440.2015. Epub 2015 Sep 25. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26408541 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insulin resistance: vascular function and exercise.Integr Med Res. 2016 Sep;5(3):198-203. doi: 10.1016/j.imr.2016.06.001. Epub 2016 Jun 9. Integr Med Res. 2016. PMID: 28462118 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aaker A, Laughlin MH. Differential adenosine sensitivity of diaphragm and skeletal muscle arterioles. J Appl Physiol. 2002;93:848–856. - PubMed
-
- Baron AD, Laakso M, Brechtel G, Hoit B, Watt C, Edelman SV. Reduced postprandial skeletal muscle blood flow contributes to glucose intolerance in human obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1990;70:1525–1533. - PubMed
-
- Baron AD, Zhu JS, Marshall S, Irsula O, Brechtel G, Keech C. Insulin resistance after hypertension induced by the nitric oxide synthesis inhibitor L-NMMA in rats. Am J Physiol. 1995;269:E709–715. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

