Protein kinase C-delta deficiency perturbs bone homeostasis by selective uncoupling of cathepsin K secretion and ruffled border formation in osteoclasts
- PMID: 22806935
- PMCID: PMC3498518
- DOI: 10.1002/jbmr.1701
Protein kinase C-delta deficiency perturbs bone homeostasis by selective uncoupling of cathepsin K secretion and ruffled border formation in osteoclasts
Abstract
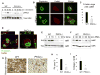
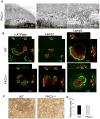
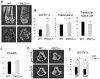
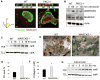
Bone homeostasis requires stringent regulation of osteoclasts, which secrete proteolytic enzymes to degrade the bone matrix. Despite recent progress in understanding how bone resorption occurs, the mechanisms regulating osteoclast secretion, and in particular the trafficking route of cathepsin K vesicles, remain elusive. Using a genetic approach, we describe the requirement for protein kinase C-delta (PKCδ) in regulating bone resorption by affecting cathepsin K exocytosis. Importantly, PKCδ deficiency does not perturb formation of the ruffled border or trafficking of lysosomal vesicles containing the vacuolar-ATPase (v-ATPase). Mechanistically, we find that cathepsin K exocytosis is controlled by PKCδ through modulation of the actin bundling protein myristoylated alanine-rich C-kinase substrate (MARCKS). The relevance of our finding is emphasized in vivo because PKCδ-/- mice exhibit increased bone mass and are protected from pathological bone loss in a model of experimental postmenopausal osteoporosis. Collectively, our data provide novel mechanistic insights into the pathways that selectively promote secretion of cathepsin K lysosomes independently of ruffled border formation, providing evidence of the presence of multiple mechanisms that regulate lysosomal exocytosis in osteoclasts.
Copyright © 2012 American Society for Bone and Mineral Research.
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors state that they have no conflicts of interest
Figures

References
-
- Blott EJ, Griffiths GM. Secretory lysosomes. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2002;3(2):122–31. - PubMed
-
- Novack DV, Teitelbaum SL. The osteoclast: friend or foe? Annu Rev Pathol. 2008;3:457–84. - PubMed
-
- Zaidi M. Skeletal remodeling in health and disease. Nat Med. 2007;13(7):791–801. - PubMed
-
- Teitelbaum SL, Ross FP. Genetic regulation of osteoclast development and function. Nature Reviews Genetics. 2003;4:638–649. - PubMed
-
- Collin O, Tracqui P, Stephanou A, Usson Y, Clement-Lacroix J, Planus E. Spatiotemporal dynamics of actin-rich adhesion microdomains: influence of substrate flexibility. J Cell Sci. 2006;119(Pt 9):1914–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

