Lipid suppression in CSI with spatial priors and highly undersampled peripheral k-space
- PMID: 22807147
- PMCID: PMC3477245
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.24399
Lipid suppression in CSI with spatial priors and highly undersampled peripheral k-space
Abstract
Mapping 1H brain metabolites using chemical shift imaging is hampered by the presence of subcutaneous lipid signals, which contaminate the metabolites by ringing due to limited spatial resolution. Even though chemical shift imaging at spatial resolution high enough to mitigate the lipid artifacts is infeasible due to signal-to-noise constraints on the metabolites, the lipid signals have orders of magnitude of higher concentration, which enables the collection of high-resolution lipid maps with adequate signal-to-noise. The previously proposed dual-density approach exploits this high signal-to-noise property of the lipid layer to suppress truncation artifacts using high-resolution lipid maps. Another recent approach for lipid suppression makes use of the fact that metabolite and lipid spectra are approximately orthogonal, and seeks sparse metabolite spectra when projected onto lipid-basis functions. This work combines and extends the dual-density approach and the lipid-basis penalty, while estimating the high-resolution lipid image from 2-average k-space data to incur minimal increase on the scan time. Further, we exploit the spectral-spatial sparsity of the lipid ring and propose to estimate it from substantially undersampled (acceleration R=10 in the peripheral k-space) 2-average in vivo data using compressed sensing and still obtain improved lipid suppression relative to using dual-density or lipid-basis penalty alone.
Copyright © 2012 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
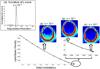
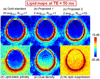
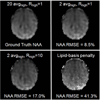


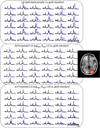

References
-
- Duyn JH, Gillen J, Sobering G, van Zijl PC, Moonen CT. Multisection proton MR spectroscopic imaging of the brain. Radiology. 1993;188(1):277–282. - PubMed
-
- Le Roux P, Gilles RJ, McKinnon GC, Carlier PG. Optimized outer volume suppression for single-shot fast spin-echo cardiac imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging. 1998;8(5):1022–1032. - PubMed
-
- Luo Y, de Graaf RA, DelaBarre L, Tannus A, Garwood M. BISTRO: an outer-volume suppression method that tolerates RF field inhomogeneity. Magn Reson Med. 2001;45(6):1095–1102. - PubMed
-
- Bydder GM, Young IR. MR imaging: clinical use of the inversion recovery sequence. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1985;9(4):659–675. - PubMed
-
- Ebel A, Govindaraju V, Maudsley AA. Comparison of inversion recovery preparation schemes for lipid suppression in 1H MRSI of human brain. Magn Reson Med. 2003;49(5):903–908. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

