The GTPase-deficient Rnd proteins are stabilized by their effectors
- PMID: 22807448
- PMCID: PMC3442376
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.327056
The GTPase-deficient Rnd proteins are stabilized by their effectors
Abstract
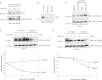
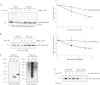
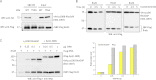
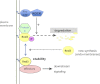
Rnd proteins are Rho family GTP-binding proteins with cellular functions that antagonize RhoA signaling. We recently described a new Rnd3 effector Syx, also named PLEKHG5, that interacts with Rnds via a Raf1-like "Ras-binding domain." Syx is a multidomain RhoGEF that participates in early zebrafish development. Here we demonstrated that Rnd1, Rnd2, and Rnd3 stability is acutely dependent on interaction with their effectors such as Syx or p190 RhoGAP. Although Rnd3 turnover is blocked by treatment of cells with MG132, we provide evidence that such turnover is mediated indirectly by effects on the Rnd3 effectors, rather than on Rnd3 itself, which is not significantly ubiquitinated. The minimal regions of Syx and p190 RhoGAP that bind Rnd3 are not sequence-related but have similar effects. We have identified features that allow for Rnd3 turnover including a conserved Lys-45 close to the switch I region and the C-terminal membrane-binding domain of Rnd3, which cannot be substituted by the equivalent Cdc42 CAAX sequence. By contrast, an effector binding-defective mutant of Rnd3 when overexpressed undergoes turnover at normal rates. Interestingly the activity of the RhoA-regulated kinase ROCK stimulates Rnd3 turnover. This study suggests that Rnd proteins are regulated through feedback mechanisms in cells where the level of effectors and RhoA activity influence the stability of Rnd proteins. This effector feedback behavior is analogous to the ability of ACK1 and PAK1 to prolong the lifetime of the active GTP-bound state of Cdc42 and Rac1.
Figures



References
-
- Chardin P. (2006) Function and regulation of Rnd proteins. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 7, 54–62 - PubMed
-
- Riou P., Villalonga P., Ridley A. J. (2010) Rnd proteins: multifunctional regulators of the cytoskeleton and cell cycle progression. Bioessays 32, 986–992 - PubMed
-
- Hansen S. H., Zegers M. M., Woodrow M., Rodriguez-Viciana P., Chardin P., Mostov K. E., McMahon M. (2000) Induced expression of Rnd3 is associated with transformation of polarized epithelial cells by the Raf-MEK-extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway. Mol. Cell. Biol. 20, 9364–9375 - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

