A randomized, double-blind placebo controlled trial of balapiravir, a polymerase inhibitor, in adult dengue patients
- PMID: 22807519
- PMCID: PMC3610419
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jis470
A randomized, double-blind placebo controlled trial of balapiravir, a polymerase inhibitor, in adult dengue patients
Abstract
Background: Dengue is the most common arboviral infection of humans. There are currently no specific treatments for dengue. Balapiravir is a prodrug of a nucleoside analogue (called R1479) and an inhibitor of hepatitis C virus replication in vivo.
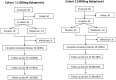
Methods: We conducted in vitro experiments to determine the potency of balapiravir against dengue viruses and then an exploratory, dose-escalating, randomized placebo-controlled trial in adult male patients with dengue with <48 hours of fever.
Results: The clinical and laboratory adverse event profile in patients receiving balapiravir at doses of 1500 mg (n = 10) or 3000 mg (n = 22) orally for 5 days was similar to that of patients receiving placebo (n = 32), indicating balapiravir was well tolerated. However, twice daily assessment of viremia and daily assessment of NS1 antigenemia indicated balapiravir did not measurably alter the kinetics of these virological markers, nor did it reduce the fever clearance time. The kinetics of plasma cytokine concentrations and the whole blood transcriptional profile were also not attenuated by balapiravir treatment.
Conclusions: Although this trial, the first of its kind in dengue, does not support balapiravir as a candidate drug, it does establish a framework for antiviral treatment trials in dengue and provides the field with a clinically evaluated benchmark molecule.
Clinical trials registration: NCT01096576.
Figures


References
-
- Suaya JA, Shepard DS, Siqueira JB, et al. Cost of Dengue cases in eight countries in the Americas and Asia: a prospective study. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2009;80:846–55. - PubMed
-
- Libraty DH, Young PR, Pickering D, et al. High circulating levels of the dengue virus nonstructural protein NS1 early in dengue illness correlate with the development of dengue hemorrhagic fever. J Infect Dis. 2002;186:1165–8. - PubMed
-
- Libraty DH, Endy TP, Houng HS, et al. Differing influences of virus burden and immune activation on disease severity in secondary dengue-3 virus infections. J Infect Dis. 2002;185:1213–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

