Global evaluation of Eph receptors and ephrins in lung adenocarcinomas identifies EphA4 as an inhibitor of cell migration and invasion
- PMID: 22807579
- PMCID: PMC3438283
- DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-12-0030
Global evaluation of Eph receptors and ephrins in lung adenocarcinomas identifies EphA4 as an inhibitor of cell migration and invasion
Abstract
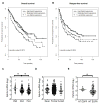
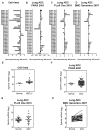
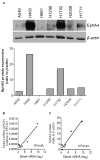
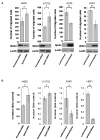
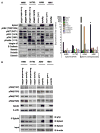
The Eph family of receptors is the largest family of receptor tyrosine kinases, but it remains poorly studied in lung cancer. We aimed to systematically explore the human Eph receptors and their ligands, the ephrins, in lung adenocarcinoma. The prognostic impact of Eph receptor and ephrin gene expression was analyzed using 2 independent cohorts of lung adenocarcinoma. Gene expression profiles in lung adenocarcinoma compared with normal adjacent lung were studied in 3 independent cohorts and in cell lines. Gene expression profiles were validated with quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) and Western blotting in cell lines. Functional studies to assess the role of Eph receptor A4 (EphA4) were carried out in vitro. The biological effects of EphA4 in lung cancer cell lines were assayed following overexpression and knockdown. Of the 11 Eph receptors and 8 ephrins analyzed, only EphA4 and ephrin A1 gene expression were consistently associated with an improved outcome in patients with lung adenocarcinoma. Expression levels of EphA4 by microarray correlated well with expression levels measured by qPCR and Western blotting. EphA4 overexpression reduced cell migration and invasion but did not affect cell cycle, apoptosis, or drug sensitivity. Surprisingly, EphA4 was expressed at higher levels in cancer compared with non-cancer tissues and cell lines. EphA4 gene expression is associated with an improved outcome in patients with resected lung adenocarcinoma, possibly by affecting cancer cell migration and invasion.
©2012 AACR.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Ramalingam SS, Owonikoko TK, Khuri FR. Lung cancer: New biological insights and recent therapeutic advances. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:91–112. - PubMed
-
- Surawska H, Ma PC, Salgia R. The role of ephrins and Eph receptors in cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2004;15:419–33. - PubMed
-
- Brannan JM, Sen B, Saigal B, Prudkin L, Behrens C, Solis L, et al. EphA2 in the early pathogenesis and progression of non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Prev Res (Phila) 2009;2:1039–49. - PubMed
-
- Brannan JM, Dong W, Prudkin L, Behrens C, Lotan R, Bekele BN, et al. Expression of the receptor tyrosine kinase EphA2 is increased in smokers and predicts poor survival in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15:4423–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

