GWAS identifies novel susceptibility loci on 6p21.32 and 21q21.3 for hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis B virus carriers
- PMID: 22807686
- PMCID: PMC3395595
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002791
GWAS identifies novel susceptibility loci on 6p21.32 and 21q21.3 for hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis B virus carriers
Abstract
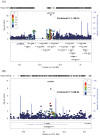
Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have recently identified KIF1B as susceptibility locus for hepatitis B virus (HBV)-related hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). To further identify novel susceptibility loci associated with HBV-related HCC and replicate the previously reported association, we performed a large three-stage GWAS in the Han Chinese population. 523,663 autosomal SNPs in 1,538 HBV-positive HCC patients and 1,465 chronic HBV carriers were genotyped for the discovery stage. Top candidate SNPs were genotyped in the initial validation samples of 2,112 HBV-positive HCC cases and 2,208 HBV carriers and then in the second validation samples of 1,021 cases and 1,491 HBV carriers. We discovered two novel associations at rs9272105 (HLA-DQA1/DRB1) on 6p21.32 (OR = 1.30, P = 1.13×10⁻¹⁹) and rs455804 (GRIK1) on 21q21.3 (OR = 0.84, P = 1.86×10⁻⁸), which were further replicated in the fourth independent sample of 1,298 cases and 1,026 controls (rs9272105: OR = 1.25, P = 1.71×10⁻⁴; rs455804: OR = 0.84, P = 6.92×10⁻³). We also revealed the associations of HLA-DRB1*0405 and 0901*0602, which could partially account for the association at rs9272105. The association at rs455804 implicates GRIK1 as a novel susceptibility gene for HBV-related HCC, suggesting the involvement of glutamate signaling in the development of HBV-related HCC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Sener SF. Disease without borders. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55:7–9. - PubMed
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, et al. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61:69–90. - PubMed
-
- Yu MW, Hsu FC, Sheen IS, Chu CM, Lin DY, et al. Prospective study of hepatocellular carcinoma and liver cirrhosis in asymptomatic chronic hepatitis B virus carriers. Am J Epidemiol. 1997;145:1039–1047. - PubMed
-
- Yu MW, Chang HC, Liaw YF, Lin SM, Lee SD, et al. Familial risk of hepatocellular carcinoma among chronic hepatitis B carriers and their relatives. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2000;92:1159–1164. - PubMed
-
- Kao JH, Chen PJ, Chen DS. Recent advances in the research of hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma: epidemiologic and molecular biological aspects. Adv Cancer Res. 2010;108:21–72. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

