A key role for Chd1 in histone H3 dynamics at the 3' ends of long genes in yeast
- PMID: 22807688
- PMCID: PMC3395613
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002811
A key role for Chd1 in histone H3 dynamics at the 3' ends of long genes in yeast
Abstract
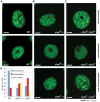
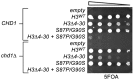
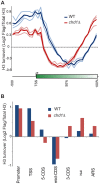
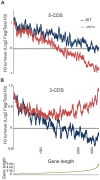
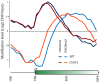
Chd proteins are ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling enzymes implicated in biological functions from transcriptional elongation to control of pluripotency. Previous studies of the Chd1 subclass of these proteins have implicated them in diverse roles in gene expression including functions during initiation, elongation, and termination. Furthermore, some evidence has suggested a role for Chd1 in replication-independent histone exchange or assembly. Here, we examine roles of Chd1 in replication-independent dynamics of histone H3 in both Drosophila and yeast. We find evidence of a role for Chd1 in H3 dynamics in both organisms. Using genome-wide ChIP-on-chip analysis, we find that Chd1 influences histone turnover at the 5' and 3' ends of genes, accelerating H3 replacement at the 5' ends of genes while protecting the 3' ends of genes from excessive H3 turnover. Although consistent with a direct role for Chd1 in exchange, these results may indicate that Chd1 stabilizes nucleosomes perturbed by transcription. Curiously, we observe a strong effect of gene length on Chd1's effects on H3 turnover. Finally, we show that Chd1 also affects histone modification patterns over genes, likely as a consequence of its effects on histone replacement. Taken together, our results emphasize a role for Chd1 in histone replacement in both budding yeast and Drosophila melanogaster, and surprisingly they show that the major effects of Chd1 on turnover occur at the 3' ends of genes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Kornberg RD, Lorch Y. Twenty-five years of the nucleosome, fundamental particle of the eukaryote chromosome. Cell. 1999;98:285–294. - PubMed
-
- Jackson V, Chalkley R. Histone synthesis and deposition in the G1 and S phases of hepatoma tissue culture cells. Biochemistry. 1985;24:6921–6930. - PubMed
-
- Rufiange A, Jacques PE, Bhat W, Robert F, Nourani A. Genome-wide replication-independent histone H3 exchange occurs predominantly at promoters and implicates H3 K56 acetylation and Asf1. Mol Cell. 2007;27:393–405. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

