STAT1 interacts with RXRα to upregulate ApoCII gene expression in macrophages
- PMID: 22808166
- PMCID: PMC3395716
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0040463
STAT1 interacts with RXRα to upregulate ApoCII gene expression in macrophages
Abstract
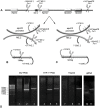
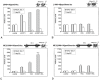
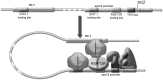
Apolipoprotein CII (apoCII) is a specific activator of lipoprotein lipase and plays an important role in triglyceride metabolism. The aim of our work was to elucidate the regulatory mechanisms involved in apoCII gene modulation in macrophages. Using Chromosome Conformation Capture we demonstrated that multienhancer 2 (ME.2) physically interacts with the apoCII promoter and this interaction facilitates the transcriptional enhancement of the apoCII promoter by the transcription factors bound on ME.2. We revealed that the transcription factor STAT1, previously shown to bind to its specific site on ME.2, is functional for apoCII gene upregulation. We found that siRNA-mediated inhibition of STAT1 gene expression significantly decreased the apoCII levels, while STAT1 overexpression in RAW 264.7 macrophages increased apoCII gene expression. Using transient transfections, DNA pull down and chromatin immunoprecipitation assays, we revealed a novel STAT1 binding site in the -500/-493 region of the apoCII promoter, which mediates apoCII promoter upregulation by STAT1. Interestingly, STAT1 could not exert its upregulatory effect when the RXRα/T3Rβ binding site located on the apoCII promoter was mutated, suggesting physical and functional interactions between these factors. Using GST pull-down and co-immunoprecipitation assays, we demonstrated that STAT1 physically interacts with RXRα. Taken together, these data revealed that STAT1 bound on ME.2 cooperates with RXRα located on apoCII promoter and upregulates apoCII expression only in macrophages, due to the specificity of the long-range interactions between the proximal and distal regulatory elements. Moreover, we showed for the first time that STAT1 and RXRα physically interact to exert their regulatory function.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Miller AL, Smith LC. Activation of lipoprotein lipase by apolipoprotein glutamic acid. Formation of a stable surface film. J Biol Chem. 1973;248:3359–3362. - PubMed
-
- Zannis VI, Kardassis D, Zanni EE. Genetic mutations affecting human lipoproteins, their receptors, and their enzymes. Adv Hum Genet. 1993;21:145–319. - PubMed
-
- Nilsson-Ehle P, Garfinkel AS, Schotz MC. Lipolytic enzymes and plasma lipoprotein metabolism. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:667–693. - PubMed
-
- Myklebost O, Williamson B, Markham AF, Myklebost SR, Rogers J, et al. The isolation and characterization of cDNA clones for human apolipoprotein CII. J Biol Chem. 1984;259:4401–4414. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

