PI3Kδ is essential for tumor clearance mediated by cytotoxic T lymphocytes
- PMID: 22808277
- PMCID: PMC3396622
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0040852
PI3Kδ is essential for tumor clearance mediated by cytotoxic T lymphocytes
Abstract
Background: PI3Kδ is a lipid kinase of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase class 1A family and involved in early signaling events of leukocytes regulating proliferation, differentiation and survival. Currently, several inhibitors of PI3Kδ are under investigation for the treatment of hematopoietic malignancies. In contrast to the beneficial effect of inhibiting PI3Kδ in tumor cells, several studies reported the requirement of PI3Kδ for the function of immune cells, such as natural killer and T helper cells. Cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) are essential for tumor surveillance. The scope of this study is to clarify the potential impact of PI3Kδ inhibition on the function of CTLs with emphasis on tumor surveillance.
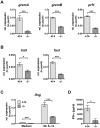
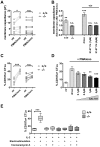
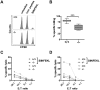
Principal findings: PI3Kδ-deficient mice develop significantly bigger tumors when challenged with MC38 colon adenocarcinoma cells. This defect is accounted for by the fact that PI3Kδ controls the secretory perforin-granzyme pathway as well as the death-receptor pathway of CTL-mediated cytotoxicity, leading to severely diminished cytotoxicity against target cells in vitro and in vivo in the absence of PI3Kδ expression. PI3Kδ-deficient CTLs express low mRNA levels of important components of the cytotoxic machinery, e.g. prf1, grzmA, grzmB, fasl and trail. Accordingly, PI3Kδ-deficient tumor-infiltrating CTLs display a phenotype reminiscent of naïve T cells (CD69(low)CD62L(high)). In addition, electrophysiological capacitance measurements confirmed a fundamental degranulation defect of PI3Kδ-/- CTLs.
Conclusion: Our results demonstrate that CTL-mediated tumor surveillance is severely impaired in the absence of PI3Kδ and predict that impaired immunosurveillance may limit the effectiveness of PI3Kδ inhibitors in long-term treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Yap TA, Garrett MD, Walton MI, Raynaud F, de Bono JS, et al. Targeting the PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway: progress, pitfalls, and promises. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2008;8:393–412. Available: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&dop.... - PubMed
-
- Fruman DA, Cantley LC. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase in immunological systems. Semin Immunol. 2002;14:7–18. Available: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&dop.... - PubMed
-
- Beer-Hammer S, Zebedin E, von Holleben M, Alferink J, Reis B, et al. The catalytic PI3K isoforms p110gamma and p110delta contribute to B cell development and maintenance, transformation, and proliferation. Journal of leukocyte biology 87: 1083–1095. 2010. Available: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20200404. Accessed 2011 July 27. - PubMed
-
- So L, Fruman DA. PI3K signalling in B- and T-lymphocytes: new developments and therapeutic advances. The Biochemical journal 442: 465–481. 2012. Available: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22364281. Accessed 2012 March 22. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jou ST, Carpino N, Takahashi Y, Piekorz R, Chao JR, et al. Essential, nonredundant role for the phosphoinositide 3-kinase p110delta in signaling by the B-cell receptor complex. Mol Cell Biol. 2002;22:8580–8591. Available: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&dop.... - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

