Intracellular calcium dynamics, shortened action potential duration, and late-phase 3 early afterdepolarization in Langendorff-perfused rabbit ventricles
- PMID: 22809087
- PMCID: PMC3479328
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1540-8167.2012.02400.x
Intracellular calcium dynamics, shortened action potential duration, and late-phase 3 early afterdepolarization in Langendorff-perfused rabbit ventricles
Abstract
Introduction: To elucidate the mechanism of late-phase 3 early after depolarization (EAD) in ventricular arrhythmogenesis, we hypothesized that intracellular calcium (Ca(i) ) overloading and action potential duration (APD) shortening may promote late-phase 3 EAD and triggered activity, leading to development of ventricular fibrillation (VF).
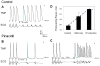
Methods and results: In isolated rabbit hearts, we performed microelectrode recording and simultaneous dual optical mapping of transmembrane potential (V(m) ) and Ca(i) transient on left ventricular endocardium. An I(KATP) channel opener, pinacidil, was used to abbreviate APD. Rapid pacing was then performed. Upon abrupt cessation of rapid pacing with cycle lengths of 60-200 milliseconds, there were APD(90) prolongation and the corresponding Ca(i) overloading in the first postpacing beats. The duration of Ca(i) transient recovered to 50% (DCaT(50) ) and 90% (DCaT(90) ) in the first postpacing beats was significantly longer than baseline. Abnormal Ca(i) elevation coupled with shortened APD produced late-phase 3 EAD induced triggered activity and VF. In additional 6 preparations, the heart tissues were treated with BAPTA-AM, a calcium chelator. BAPTA-AM significantly reduced the maximal Ca(i) amplitude (26.4 ± 3.5% of the control; P < 0.001) and the duration of Ca(i) transients in the mapped region, preventing the development of EAD and triggered activity that initiated VF.
Conclusions: I (KATP) channel activation along with Ca(i) overloading are associated with the development of late-phase 3 EAD and VF. Because acute myocardial ischemia activates the I(KATP) channel, late-phase 3 EADs may be a mechanism for VF initiation during acute myocardial ischemia.
© 2012 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures




Comment in
-
Calcium and arrhythmias: ignore at your peril.J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2012 Dec;23(12):1372-3. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8167.2012.02423.x. Epub 2012 Nov 6. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2012. PMID: 23131105 No abstract available.
References
-
- Uchida T, Yashima M, Gotoh M, Qu Z, Garfinkel A, Weiss JN, Fishbein MC, Mandel WJ, Chen P-S, Karagueuzian HS. Mechanism of acceleration of functional reentry in the ventricle: effects of ATP-sensitive potassium channel opener. Circulation. 1999;99:704–712. - PubMed
-
- Coromilas J, Costeas C, Deruyter B, Dillon SM, Peters NS, Wit AL. Effects of pinacidil on electrophysiological properties of epicardial border zone of healing canine infarcts: possible effects of K(ATP) channel activation. Circulation. 2002;105:2309–2317. - PubMed
-
- Arena JP, Kass RS. Enhancement of potassium-sensitive current in heart cells by pinacidil. Evidence for modulation of the ATP-sensitive potassium channel. Circ Res. 1989;65:436–445. - PubMed
-
- Traverse JH, Chen Y, Hou M, Li Y, Bache RJ. Effect of K+ATP channel and adenosine receptor blockade during rest and exercise in congestive heart failure. Circ Res. 2007;100:1643–1649. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

