Association of low plasma adiponectin with early diastolic dysfunction
- PMID: 22809257
- PMCID: PMC3646250
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1751-7133.2011.00276.x
Association of low plasma adiponectin with early diastolic dysfunction
Abstract
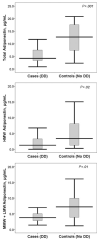
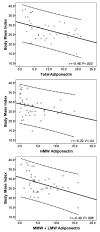
Diastolic dysfunction (DD) with preserved left ventricular (LV) ejection fraction (EF) has been linked to obesity. Adiponectin is a cytokine related to obesity and obesity-linked cardiovascular complications. The authors aimed to determine the independent association of DD with adiponectin. Fifty patients with impaired relaxation DD and a normal EF and age-matched normal controls were recruited. Plasma levels of total and high molecular weight (HMW) adiponectin were measured. Mid and low molecular weight (MMW+LMW) fractions of adiponectin were calculated by subtracting HMW fraction from total adiponectin. The DD group had significantly lower total (median, 4.4 vs 12.7 μg/mL; P=.001), HMW fraction (median, 1.3 vs 3.4 μg/mL; P=.02), and MMW+LMW fraction of adiponectin (median, 3.8 vs 7.2 μg/mL; P=.01). Body mass index (BMI) negatively correlated with total (r:-0.46, P=.003), HMW (r:-0.32, P=.038), and MMW+LMW (r:-0.40, P=.006) fractions of adiponectin. DD had an independent association with both BMI (P<.05) and total adiponectin (P<.001) in linear regression model using sex, BMI, blood pressure, and total adiponectin as covariates. DD was associated with BMI (P=.02), HMW fraction (P=.03), and MMW+LMW fraction (P=.004) in similar linear regression analyses. Adiponectin deficiency may be one explanation for the adiposity-related cardiac oxidation known to be involved in the pathogenesis of DD.
© 2011 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Adiponectin multimeric forms but not total adiponectin levels are associated with myocardial infarction in non-diabetic men.J Atheroscler Thromb. 2011;18(7):616-27. doi: 10.5551/jat.8359. Epub 2011 Apr 21. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2011. PMID: 21512277
-
Low adiponectin is associated with diastolic dysfunction in women: a cross-sectional study from the Tromsø Study.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2017 Mar 14;17(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s12872-017-0509-2. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2017. PMID: 28292262 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal serum adiponectin multimers in preeclampsia.J Perinat Med. 2009;37(4):349-63. doi: 10.1515/JPM.2009.085. J Perinat Med. 2009. PMID: 19348608 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal serum adiponectin multimers in gestational diabetes.J Perinat Med. 2009;37(6):637-50. doi: 10.1515/JPM.2009.101. J Perinat Med. 2009. PMID: 19530957 Free PMC article.
-
Low-molecular-weight adiponectin and high-molecular-weight adiponectin levels in relation to diabetes.Obesity (Silver Spring). 2014 Feb;22(2):401-7. doi: 10.1002/oby.20553. Epub 2013 Sep 10. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2014. PMID: 23818415
Cited by
-
Proteomic Correlates of the Urinary Protein/Creatinine Ratio in Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction.Am J Cardiol. 2023 Nov 1;206:312-319. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2023.08.146. Epub 2023 Sep 19. Am J Cardiol. 2023. PMID: 37734292 Free PMC article.
-
The Significance of the Effect of Visceral Adiposity on Left Ventricular Diastolic Function in the General Population.Sci Rep. 2019 Mar 14;9(1):4435. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-37137-x. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30872595 Free PMC article.
-
Low-molecular-weight adiponectin is more closely associated with disease activity of rheumatoid arthritis than other adiponectin multimeric forms.Clin Rheumatol. 2015 Jun;34(6):1025-30. doi: 10.1007/s10067-015-2899-9. Epub 2015 Mar 10. Clin Rheumatol. 2015. PMID: 25750183
-
Effects of Adiponectin on Diastolic Function in Mice Underwent Transverse Aorta Constriction.J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2020 Apr;13(2):225-237. doi: 10.1007/s12265-019-09913-1. Epub 2019 Oct 16. J Cardiovasc Transl Res. 2020. PMID: 31621035 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation analysis of the triglyceride glucose index and heart failure with preserved ejection fraction in essential hypertensive patients.Clin Cardiol. 2022 Sep;45(9):936-942. doi: 10.1002/clc.23881. Epub 2022 Jun 29. Clin Cardiol. 2022. PMID: 35770315 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Owan TE, Hodge DO, Herges RM, et al. Trends in the prevalence and outcome of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:251–259. - PubMed
-
- Zile MR, Brutsaert DL. New concepts in diastolic dysfunction and diastolic heart failure: part I: diagnosis, prognosis, and measurements of diastolic function. Circulation. 2002;105:1387–1393. - PubMed
-
- Bhatia RS, Tu JV, Lee DS, et al. Outcome of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction in a population-based study. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:260–269. - PubMed
-
- Massie BM, Carson PE, McMurray JJ, I-PRESERVE Investigators Irbesartan in patients with heart failure and preserved ejection fraction. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:2456–2467. - PubMed
-
- Yusuf S, Pfeffer MA, Swedberg K, et al. The CHARM Investigators and Committees. Effects of candesartan in patients with chronic heart failure and preserved left-ventricular ejection fraction: the CHARM Preserved Trial. Lancet. 2003;362:777–781. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

