Distinctive patterns of alterations in proton efflux from goldfish retinal horizontal cells monitored with self-referencing H⁺-selective electrodes
- PMID: 22809323
- PMCID: PMC11342235
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2012.08226.x
Distinctive patterns of alterations in proton efflux from goldfish retinal horizontal cells monitored with self-referencing H⁺-selective electrodes
Abstract
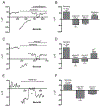
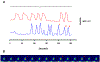
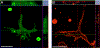
The H(+) hypothesis of lateral feedback inhibition in the outer retina predicts that depolarizing agents should increase H(+) release from horizontal cells. To test this hypothesis, self-referencing H(+) -selective microelectrodes were used to measure extracellular H(+) fluxes from isolated goldfish horizontal cells. We found a more complex pattern of cellular responses than previously observed from horizontal cells of other species examined using this technique. One class of cells had an initial standing signal indicative of high extracellular H(+) adjacent to the cell membrane; challenge with glutamate, kainate or high extracellular potassium induced an extracellular alkalinization. This alkalinization was reduced by the calcium channel blockers nifedipine and cobalt. A second class of cells displayed spontaneous oscillations in extracellular H(+) that were abolished by cobalt, nifedipine and low extracellular calcium. A strong correlation between changes in intracellular calcium and extracellular proton flux was detected in experiments simultaneously monitoring intracellular calcium and extracellular H(+) . A third set of cells was characterized by a standing extracellular alkalinization which was turned into an acidic signal by cobalt. In this last set of cells, addition of glutamate or high extracellular potassium did not significantly alter the proton signal. Taken together, the response characteristics of all three sets of neurons are most parsimoniously explained by activation of a plasma membrane Ca(2+) ATPase pump, with an extracellular alkalinization resulting from exchange of intracellular calcium for extracellular H(+) . These findings argue strongly against the hypothesis that H(+) release from horizontal cells mediates lateral inhibition in the outer retina.
© 2012 The Authors. European Journal of Neuroscience © 2012 Federation of European Neuroscience Societies and Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Fluorescent imaging reports an extracellular alkalinization induced by glutamatergic activation of isolated retinal horizontal cells.J Neurophysiol. 2014 Mar;111(5):1056-64. doi: 10.1152/jn.00768.2013. Epub 2013 Dec 11. J Neurophysiol. 2014. PMID: 24335210 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of extracellular proton fluxes from retinal horizontal cells of the catfish by depolarization and glutamate.J Gen Physiol. 2007 Aug;130(2):169-82. doi: 10.1085/jgp.200709737. J Gen Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17664345 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular pH dynamics of retinal horizontal cells examined using electrochemical and fluorometric methods.J Neurophysiol. 2012 Feb;107(3):868-79. doi: 10.1152/jn.00878.2011. Epub 2011 Nov 16. J Neurophysiol. 2012. PMID: 22090459 Free PMC article.
-
Proton-mediated feedback inhibition of presynaptic calcium channels at the cone photoreceptor synapse.J Neurosci. 2005 Apr 20;25(16):4108-17. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5253-04.2005. J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 15843613 Free PMC article.
-
Cooperative electrogenic proton transport pathways in the plasma membrane of the proton-secreting osteoclast.Pflugers Arch. 2018 Jun;470(6):851-866. doi: 10.1007/s00424-018-2137-9. Epub 2018 Mar 17. Pflugers Arch. 2018. PMID: 29550927 Review.
Cited by
-
Fluorescent imaging reports an extracellular alkalinization induced by glutamatergic activation of isolated retinal horizontal cells.J Neurophysiol. 2014 Mar;111(5):1056-64. doi: 10.1152/jn.00768.2013. Epub 2013 Dec 11. J Neurophysiol. 2014. PMID: 24335210 Free PMC article.
-
Complexin regulation of synaptic vesicle release: mechanisms in the central nervous system and specialized retinal ribbon synapses.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Dec 3;22(1):581. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01942-x. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 39627811 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activation of retinal glial (Müller) cells by extracellular ATP induces pronounced increases in extracellular H+ flux.PLoS One. 2018 Feb 21;13(2):e0190893. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0190893. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29466379 Free PMC article.
-
Engaging Undergraduates in a Unique Neuroscience Research Opportunity: A Collaborative Research Experience Between a Primarily Undergraduate Institution (PUI) and a Major Research Institution.J Undergrad Neurosci Educ. 2013 Oct 15;12(1):A85-92. eCollection 2013. J Undergrad Neurosci Educ. 2013. PMID: 24319396 Free PMC article.
-
Spontaneous action potentials in retinal horizontal cells of goldfish (Carassius auratus) are dependent upon L-type Ca2+ channels and ryanodine receptors.J Neurophysiol. 2019 Dec 1;122(6):2284-2293. doi: 10.1152/jn.00240.2019. Epub 2019 Oct 9. J Neurophysiol. 2019. PMID: 31596629 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akopian A, Krizaj D & Witkovsky P (1997) Both high- and low voltage-activated calcium currents contribute to the light-evoked responses of luminosity horizontal cells in the Xenopus retina. Brain Res., 762, 121–130. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

