Nano-sized manganese oxides as biomimetic catalysts for water oxidation in artificial photosynthesis: a review
- PMID: 22809849
- PMCID: PMC3427528
- DOI: 10.1098/rsif.2012.0412
Nano-sized manganese oxides as biomimetic catalysts for water oxidation in artificial photosynthesis: a review
Abstract
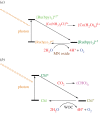
There has been a tremendous surge in research on the synthesis of various metal compounds aimed at simulating the water-oxidizing complex (WOC) of photosystem II (PSII). This is crucial because the water oxidation half reaction is overwhelmingly rate-limiting and needs high over-voltage (approx. 1 V), which results in low conversion efficiencies when working at current densities required for hydrogen production via water splitting. Particular attention has been given to the manganese compounds not only because manganese has been used by nature to oxidize water but also because manganese is cheap and environmentally friendly. The manganese-calcium cluster in PSII has a dimension of about approximately 0.5 nm. Thus, nano-sized manganese compounds might be good structural and functional models for the cluster. As in the nanometre-size of the synthetic models, most of the active sites are at the surface, these compounds could be more efficient catalysts than micrometre (or bigger) particles. In this paper, we focus on nano-sized manganese oxides as functional and structural models of the WOC of PSII for hydrogen production via water splitting and review nano-sized manganese oxides used in water oxidation by some research groups.
Figures
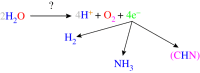


References
-
- Wydrzynski T., Hillier W. (eds) 2011. Molecular solar fuels. Cambridge, UK: Royal Society of Cambridge
-
- Najafpour M. M. (ed.) 2012. Artificial photosynthesis. Rijeka, Croatia: Tech Publications
-
- Pace R. J. 2005. An integrated artificial photosynthesis model. In Artificial photosynthesis from basic biology to industrial application (eds Collings A. F., Critchley C.), ch. 2 Weinheim, Germany: Wiley-VCH
-
- Reece S. Y., Hamel J. A., Sung K., Jarvil T. D., Esswein A. J., Pijpers J. J. H., Nocera D. G. 2011. Wireless solar water splitting using silicon-based semiconductors and earth-abundant catalysts. Science 334, 645–64810.1126/science.1209816 (doi:10.1126/science.1209816) - DOI - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lewis N. S. 2007. Toward cost-effective solar energy use. Science 315, 798–80110.1126/science.1137014 (doi:10.1126/science.1137014) - DOI - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

