Cellular strain amplifies LPS-induced stress signaling in immature enterocytes: potential implications for preterm infant NCPAP
- PMID: 22810014
- PMCID: PMC3612960
- DOI: 10.1038/pr.2012.77
Cellular strain amplifies LPS-induced stress signaling in immature enterocytes: potential implications for preterm infant NCPAP
Abstract
Background: Recent clinical observations of increased necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) incidence in some nasal continuous positive airway pressure (NCPAP) patients raise concerns about whether the related abdominal distension is benign or contributes to NEC. We tested the hypothesis that mechanical strain causes an exaggerated enterocyte inflammatory response and decreased enterocyte growth and proliferation in the absence and presence of lipopolysaccharide (LPS).
Methods: First we used a confluent enterocyte (IEC-6) monolayer to investigate effects of strain on inflammatory cytokine production and Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR-4) gene expression. Then we used a low seeding density to measure cell growth and proliferation. Ten percent mechanical strain was applied.
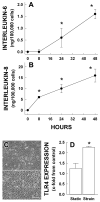
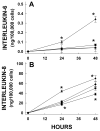
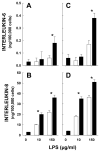
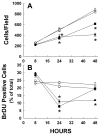
Results: Significant increases in interleukin (IL)-8 and in IL-6 were observed after 8 and 24 h of cellular strain, respectively, and maintained throughout the study. TLR-4 expression was increased at 48 h. Mechanical strain led to slower proliferation and division whereas LPS alone had minimal effects. The responses of LPS and strain were supra-additive, suggesting synergistic cellular effects.
Conclusion: We speculate intestinal distension associated with the use of NCPAP, especially in the presence of abnormal gut colonization, may result in increased inflammatory cytokine production and be a contributing factor to neonatal intestinal morbidities.
Figures
References
-
- Halamek L, Morley C. Continuous positive airway pressure during neonatal resuscitation. Clin Perinatol. 2006;33:83–98. vii. - PubMed
-
- Meyer M, Mildenhall L, Wong M. Outcomes for infants weighting less than 1000 grams cared for with a nasal continuous positive airway pressure-based strategy. J Paediatr Child Health. 2004;40:38–41. - PubMed
-
- Aly H, Milner JD, Patel K, et al. Does the experience with the use of nasal continuous positive airway pressure improve over time in extremely low birth weight infants? Pediatrics. 2004;114:697–702. - PubMed
-
- De Klerk A, De Klerk R. Nasal continuous positive airway pressure and outcomes of preterm infants. J Paediatr Child Health. 2001;37:161–167. - PubMed
-
- Morley C, Davis P, Doyle L, et al. Nasal CPAP or intubation at birth for very preterm infants. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:700–708. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

