A nuclear Argonaute promotes multigenerational epigenetic inheritance and germline immortality
- PMID: 22810588
- PMCID: PMC3509936
- DOI: 10.1038/nature11352
A nuclear Argonaute promotes multigenerational epigenetic inheritance and germline immortality
Abstract
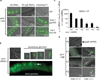
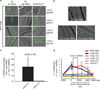
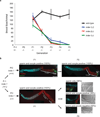
Epigenetic information is frequently erased near the start of each new generation. In some cases, however, epigenetic information can be transmitted from parent to progeny (multigenerational epigenetic inheritance). A particularly notable example of this type of epigenetic inheritance is double-stranded RNA-mediated gene silencing in Caenorhabditis elegans. This RNA-mediated interference (RNAi) can be inherited for more than five generations. To understand this process, here we conduct a genetic screen for nematodes defective in transmitting RNAi silencing signals to future generations. This screen identified the heritable RNAi defective 1 (hrde-1) gene. hrde-1 encodes an Argonaute protein that associates with small interfering RNAs in the germ cells of progeny of animals exposed to double-stranded RNA. In the nuclei of these germ cells, HRDE-1 engages the nuclear RNAi defective pathway to direct the trimethylation of histone H3 at Lys 9 (H3K9me3) at RNAi-targeted genomic loci and promote RNAi inheritance. Under normal growth conditions, HRDE-1 associates with endogenously expressed short interfering RNAs, which direct nuclear gene silencing in germ cells. In hrde-1- or nuclear RNAi-deficient animals, germline silencing is lost over generational time. Concurrently, these animals exhibit steadily worsening defects in gamete formation and function that ultimately lead to sterility. These results establish that the Argonaute protein HRDE-1 directs gene-silencing events in germ-cell nuclei that drive multigenerational RNAi inheritance and promote immortality of the germ-cell lineage. We propose that C. elegans use the RNAi inheritance machinery to transmit epigenetic information, accrued by past generations, into future generations to regulate important biological processes.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Transgenerational Epigenetic Inheritance Is Negatively Regulated by the HERI-1 Chromodomain Protein.Genetics. 2018 Dec;210(4):1287-1299. doi: 10.1534/genetics.118.301456. Epub 2018 Nov 2. Genetics. 2018. PMID: 30389807 Free PMC article.
-
The RNAi Inheritance Machinery of Caenorhabditis elegans.Genetics. 2017 Jul;206(3):1403-1416. doi: 10.1534/genetics.116.198812. Epub 2017 May 22. Genetics. 2017. PMID: 28533440 Free PMC article.
-
MORC-1 Integrates Nuclear RNAi and Transgenerational Chromatin Architecture to Promote Germline Immortality.Dev Cell. 2017 May 22;41(4):408-423.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2017.04.023. Dev Cell. 2017. PMID: 28535375 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct nuclear and cytoplasmic machineries cooperatively promote the inheritance of RNAi in Caenorhabditis elegans.Biol Cell. 2018 Oct;110(10):217-224. doi: 10.1111/boc.201800031. Epub 2018 Sep 9. Biol Cell. 2018. PMID: 30132958 Review.
-
Connecting the Dots: Linking Caenorhabditis elegans Small RNA Pathways and Germ Granules.Trends Cell Biol. 2021 May;31(5):387-401. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2020.12.012. Epub 2021 Jan 29. Trends Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 33526340 Review.
Cited by
-
Noncanonical inheritance of phenotypic information by protein amyloids.Nat Cell Biol. 2024 Oct;26(10):1712-1724. doi: 10.1038/s41556-024-01494-9. Epub 2024 Sep 2. Nat Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 39223373
-
C. elegans Heterochromatin Factor SET-32 Plays an Essential Role in Transgenerational Establishment of Nuclear RNAi-Mediated Epigenetic Silencing.Cell Rep. 2018 Nov 20;25(8):2273-2284.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.10.086. Cell Rep. 2018. PMID: 30463021 Free PMC article.
-
Transgenerational Effects of Extended Dauer Diapause on Starvation Survival and Gene Expression Plasticity in Caenorhabditis elegans.Genetics. 2018 Sep;210(1):263-274. doi: 10.1534/genetics.118.301250. Epub 2018 Jul 26. Genetics. 2018. PMID: 30049782 Free PMC article.
-
Transgenerational Epigenetic Inheritance Is Negatively Regulated by the HERI-1 Chromodomain Protein.Genetics. 2018 Dec;210(4):1287-1299. doi: 10.1534/genetics.118.301456. Epub 2018 Nov 2. Genetics. 2018. PMID: 30389807 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental Plasticity and Cellular Reprogramming in Caenorhabditis elegans.Genetics. 2019 Nov;213(3):723-757. doi: 10.1534/genetics.119.302333. Genetics. 2019. PMID: 31685551 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Reik W, Dean W, Walter J. Epigenetic reprogramming in mammalian development. Science. 2001 Aug 10;293(5532):1089–1093. - PubMed
-
- Jablonka E, Raz G. Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance: prevalence, mechanisms, and implications for the study of heredity and evolution. Q Rev Biol. 2009 Jun;84(2):131–176. - PubMed
-
- Fire A, Xu S, Montgomery MK, Kostas SA, Driver SE, Mello CC. Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 1998 Feb 19;391(6669):806–811. - PubMed
-
- Grishok A, Tabara H, Mello CC. Genetic requirements for inheritance of RNAi in C. elegans. Science. 2000 Mar 31;287(5462):2494–2497. - PubMed
-
- Vastenhouw NL, Brunschwig K, Okihara KL, Muller F, Tijsterman M, Plasterk RH. Gene expression: long-term gene silencing by RNAi. Nature. 2006 Aug 24;442(7105):882. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

