Neocortical dendritic complexity is controlled during development by NOMA-GAP-dependent inhibition of Cdc42 and activation of cofilin
- PMID: 22810622
- PMCID: PMC3418591
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.191593.112
Neocortical dendritic complexity is controlled during development by NOMA-GAP-dependent inhibition of Cdc42 and activation of cofilin
Abstract
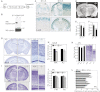
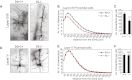
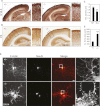
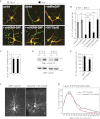
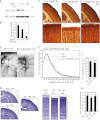
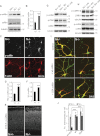
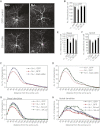
Neocortical neurons have highly branched dendritic trees that are essential for their function. Indeed, defects in dendritic arborization are associated with human neurodevelopmental disorders. The molecular mechanisms regulating dendritic arbor complexity, however, are still poorly understood. Here, we uncover the molecular basis for the regulation of dendritic branching during cortical development. We show that during development, dendritic branching requires post-mitotic suppression of the RhoGTPase Cdc42. By generating genetically modified mice, we demonstrate that this is catalyzed in vivo by the novel Cdc42-GAP NOMA-GAP. Loss of NOMA-GAP leads to decreased neocortical volume, associated specifically with profound oversimplification of cortical dendritic arborization and hyperactivation of Cdc42. Remarkably, dendritic complexity and cortical thickness can be partially restored by genetic reduction of post-mitotic Cdc42 levels. Furthermore, we identify the actin regulator cofilin as a key regulator of dendritic complexity in vivo. Cofilin activation during late cortical development depends on NOMA-GAP expression and subsequent inhibition of Cdc42. Strikingly, in utero expression of active cofilin is sufficient to restore postnatal dendritic complexity in NOMA-GAP-deficient animals. Our findings define a novel cell-intrinsic mechanism to regulate dendritic branching and thus neuronal complexity in the cerebral cortex.
Figures
Comment in
-
Regulation of dendritic branching by Cdc42 GAPs.Genes Dev. 2012 Aug 1;26(15):1653-8. doi: 10.1101/gad.199034.112. Genes Dev. 2012. PMID: 22855828 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aizawa H, Wakatsuki S, Ishii A, Moriyama K, Sasaki Y, Ohashi K, Sekine-Aizawa Y, Sehara-Fujisawa A, Mizuno K, Goshima Y, et al. 2001. Phosphorylation of cofilin by LIM-kinase is necessary for semaphorin 3A-induced growth cone collapse. Nat Neurosci 4: 367–373 - PubMed
-
- Arber S, Barbayannis FA, Hanser H, Schneider C, Stanyon CA, Bernard O, Caroni P 1998. Regulation of actin dynamics through phosphorylation of cofilin by LIM-kinase. Nature 393: 805–809 - PubMed
-
- Armstrong DD, Dunn K, Antalffy B 1998. Decreased dendritic branching in frontal, motor and limbic cortex in Rett syndrome compared with trisomy 21. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 57: 1013–1017 - PubMed
-
- Bauman ML, Kemper TL, Arin DM 1995. Pervasive neuroanatomic abnormalities of the brain in three cases of Rett's syndrome. Neurology 45: 1581–1586 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
