Serum antioxidant concentrations and metabolic syndrome are associated among U.S. adolescents in recent national surveys
- PMID: 22810988
- PMCID: PMC3417831
- DOI: 10.3945/jn.112.160416
Serum antioxidant concentrations and metabolic syndrome are associated among U.S. adolescents in recent national surveys
Abstract
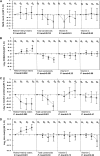
Specific micronutrients, including retinol, retinyl esters, carotenoids [α-carotene, β-carotene (cis+trans), β-cryptoxanthin, lutein+zeaxanthin, and total lycopene], vitamin E, and vitamin C have antiinflammatory and antioxidant effects, properties shown to reduce oxidative stress, a process that accompanies the pathogenesis of many chronic diseases. It is still largely unknown whether they are associated with the occurrence of metabolic syndrome (MetS) in the adolescent U.S. population. MetS was defined by the International Diabetes Federation (IDF) criteria. Other non-MetS outcomes relying on blood measurements were elevated HOMA-IR, C-reactive protein (CRP), and hyperuricemia. We tested associations between serum antioxidants and MetS outcomes among adolescents aged 12-19 y using cross-sectional data from NHANES 2001-2006 (n = 782-4285). IDF MetS prevalence was estimated at 7% among boys and 3% among girls. In adjusted models, adolescents with MetS had consistently lower carotenoid concentrations compared with their counterparts without MetS. Total carotenoids were also inversely related to HOMA-IR and CRP. Vitamin C was inversely related to uric acid level and MetS binary outcome. Retinol+retinyl esters exhibited an inverse relationship with CRP and a positive relationship with uric acid and HOMA-IR as well as MetS binary outcome. Vitamin E had no association with MetS, particularly after controlling for serum cholesterol and TG. In conclusion, among U.S. adolescents, serum carotenoid concentrations were inversely associated with MetS status, HOMA-IR, and CRP, whereas serum vitamin C was inversely related to MetS status and serum uric acid. Vitamin E had no consistent association with MetS, whereas retinol+retinyl esters had a positive relationship with HOMA-IR, uric acid, and MetS, while being inversely related to CRP. These associations need further study.
Conflict of interest statement
Author disclosures: M. A. Beydoun, J. A. Canas, H. A. Beydoun, X. Chen, M. R. Shroff, and A. B. Zonderman, no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Isomaa B, Almgren P, Tuomi T, Forsen B, Lahti K, Nissen M, Taskinen MR, Groop L. Cardiovascular morbidity and mortality associated with the metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Care. 2001;24:683–9 - PubMed
-
- Trevisan M, Liu J, Bahsas FB, Menotti A. Syndrome X and mortality: a population-based study. Risk Factor and Life Expectancy Research Group. Am J Epidemiol. 1998;148:958–66 - PubMed
-
- Wilson PW, Kannel WB, Silbershatz H, D'Agostino RB. Clustering of metabolic factors and coronary heart disease. Arch Intern Med. 1999;159:1104–9 - PubMed
-
- Haffner SM, Valdez RA, Hazuda HP, Mitchell BD, Morales PA, Stern MP. Prospective analysis of the insulin-resistance syndrome (syndrome X). Diabetes. 1992;41:715–22 - PubMed
-
- Lakka HM, Laaksonen DE, Lakka TA, Niskanen LK, Kumpusalo E, Tuomilehto J, Salonen JT. The metabolic syndrome and total and cardiovascular disease mortality in middle-aged men. JAMA. 2002;288:2709–16 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

