Transcriptional signatures mediated by acetylation overlap with early-stage Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 22811216
- PMCID: PMC3678955
- DOI: 10.1007/s00221-012-3172-y
Transcriptional signatures mediated by acetylation overlap with early-stage Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
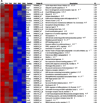
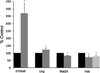
The mechanisms by which environmental influences lead to the development of complex neurodegenerative diseases are largely unknown. It is known, however, that epigenetic mechanisms can mediate alterations in transcription due to environmental influences. In order to identify genes susceptible to regulation in the adult cortex by one type of epigenetic mechanism, histone, and protein acetylation, we treated mice with the histone deacetylase inhibitor Trichostatin A (TSA). After 1 week of treatment with TSA, RNA was extracted from the brain cortices of mice and gene expression differences were analyzed by microarray profiling. The altered genes were then compared with genes differentially expressed in microarray studies of disease by database and literature searches. Genes regulated by TSA were found to significantly overlap with differentially expressed genes in the Alzheimer's disease (AD) brain. Several TSA-regulated genes involved in chromatin remodeling and epigenetic reprogramming including histone cluster 1, H4 h (Hist1H4 h), methionine adenosyltransferase II, alpha (Mat2a), and 5-methyltetrahydrofolate homocysteine reductase (Mtrr) overlapped with genes altered in early-stage AD in gray matter. We also show that the expression of hemoglobin, which has been shown to be altered in neurons in the AD brain, is regulated by TSA treatment. This analysis suggests involvement of epigenetic mechanisms in neurons in early stages of AD.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Reversible epigenetic histone modifications and Bdnf expression in neurons with aging and from a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.Age (Dordr). 2013 Jun;35(3):519-31. doi: 10.1007/s11357-011-9375-5. Epub 2012 Jan 12. Age (Dordr). 2013. PMID: 22237558 Free PMC article.
-
[Epigenetic mechanisms and alcohol use disorders: a potential therapeutic target].Biol Aujourdhui. 2017;211(1):83-91. doi: 10.1051/jbio/2017014. Epub 2017 Jul 6. Biol Aujourdhui. 2017. PMID: 28682229 Review. French.
-
Treatment of buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) donor cells with trichostatin A and 5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine alters their growth characteristics, gene expression and epigenetic status and improves the in vitro developmental competence, quality and epigenetic status of cloned embryos.Reprod Fertil Dev. 2016 Apr;28(6):824-37. doi: 10.1071/RD14176. Reprod Fertil Dev. 2016. PMID: 25409339
-
Inhibition of MMTV transcription by HDAC inhibitors occurs independent of changes in chromatin remodeling and increased histone acetylation.Oncogene. 2003 Jul 31;22(31):4807-18. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1206722. Oncogene. 2003. PMID: 12894222
-
Epigenetic targeting of histone deacetylase: therapeutic potential in Parkinson's disease?Pharmacol Ther. 2013 Oct;140(1):34-52. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2013.05.010. Epub 2013 May 24. Pharmacol Ther. 2013. PMID: 23711791 Review.
Cited by
-
Abnormal protein post-translational modifications induces aggregation and abnormal deposition of protein, mediating neurodegenerative diseases.Cell Biosci. 2024 Feb 12;14(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s13578-023-01189-y. Cell Biosci. 2024. PMID: 38347638 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lower brain and blood nutrient status in Alzheimer's disease: Results from meta-analyses.Alzheimers Dement (N Y). 2017 Jun 24;3(3):416-431. doi: 10.1016/j.trci.2017.06.002. eCollection 2017 Sep. Alzheimers Dement (N Y). 2017. PMID: 29067348 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Systems Biology Approach for Hypothesizing the Effect of Genetic Variants on Neuroimaging Features in Alzheimer's Disease.J Alzheimers Dis. 2021;80(2):831-840. doi: 10.3233/JAD-201397. J Alzheimers Dis. 2021. PMID: 33554913 Free PMC article.
-
Histone Acetylation Modifiers in the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer's Disease.Front Cell Neurosci. 2015 Jun 16;9:226. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2015.00226. eCollection 2015. Front Cell Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26136662 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Environmental enrichment prevents Aβ oligomer-induced synaptic dysfunction through mirna-132 and hdac3 signaling pathways.Neurobiol Dis. 2020 Feb;134:104617. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2019.104617. Epub 2019 Oct 24. Neurobiol Dis. 2020. PMID: 31669733 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anekonda TS, Reddy PH. Neuronal protection by sirtuins in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurochem. 2006;96:305–313. - PubMed
-
- Ballas N, Mandel G. The many faces of REST oversee epigenetic programming of neuronal genes. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2005;15:500–506. - PubMed
-
- Berger SL. The complex language of chromatin regulation during transcription. Nature. 2007;447:407–412. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

