Synthesis and evaluation of a new series of tri-, di-, and mono-N-alkylcarbamylphloroglucinols as conformationally constrained inhibitors of cholesterol esterase
- PMID: 22811279
- PMCID: PMC3631363
- DOI: 10.1002/pro.2121
Synthesis and evaluation of a new series of tri-, di-, and mono-N-alkylcarbamylphloroglucinols as conformationally constrained inhibitors of cholesterol esterase
Abstract
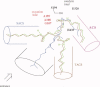
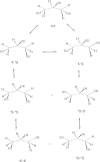
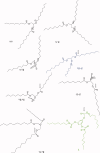
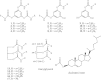
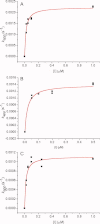
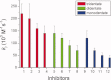
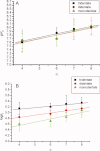
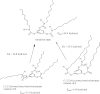
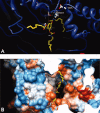
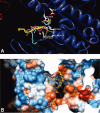
1,3,5-Tri-N-alkylcarbamylphloroglucinols (1-4) are synthesized as conformationally constrained analogs of triacylglycerols (TGs) to probe Jenck's proximity effect in the cholesterol esterase inhibition. For the cholesterol esterase inhibition, inhibitors 1-4 are 220-760-fold more potent than 1,2,3-tri-N-alkylcarbamylglycerols (13-15) that are substrate analogs of TG. Comparison of tridentate inhibitors 1-4, bidentate inhibitors 3,5-di-N-n-alkylcarbamyloxyphenols (5-8) and monodentate inhibitors 5-N-n-alkylcarbamyloxyresorcinols (9-12) indicates that inhibitory potencies are as followed: tridentate inhibitor > bidentate inhibitor > monodentate inhibitor. The log k(i) and pK(i) values of tridentate inhibitors, bidentate inhibitors, and monodentate inhibitors are linearly correlated with the alkyl chain length indicating a common mechanism in each inhibition. Also, positive slopes of these correlations indicate that the longer chain inhibitors bind more tightly to the enzyme than the shorter ones. Molecular dockings of tridentate 1, bidentate 5, and monodentate 9 into the X-ray crystal structure of cholesterol esterase suggest that one carbamyl group in the cis form of the inhibitor binds to the acyl chain-binding site of the enzyme. The second carbamyl groups in the trans forms of inhibitors 1 and 5 bind to the second acyl chain-binding site of the enzyme. The third carbamyl group in the trans form of inhibitor 1 binds to the third acyl chain-binding site of the enzyme. Moreover, the configuration of the inhibitor in the enzyme-inhibitor complex is the (1,3,5)-(cis, trans, trans)-tricarbamate form that mimics the (+gauche, -gauche)-conformation of TG.
Copyright © 2012 The Protein Society.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Structure-reactivity relationships for the inhibition mechanism at the second alkyl-chain-binding site of cholesterol esterase and lipase.Biochemistry. 1999 Aug 3;38(31):9971-81. doi: 10.1021/bi982775e. Biochemistry. 1999. PMID: 10433704
-
Synthesis and evaluation of a new series of tri-, di-, and mono-N-alkylcarbamylphloroglucinols as bulky inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase.Chem Res Toxicol. 2012 Jul 16;25(7):1462-71. doi: 10.1021/tx300119a. Epub 2012 Jun 25. Chem Res Toxicol. 2012. PMID: 22690874
-
Structure-reactivity probes for active site shapes of cholesterol esterase by carbamate inhibitors.Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999 May 18;1431(2):500-11. doi: 10.1016/s0167-4838(99)00073-4. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999. PMID: 10350625
-
Quantitative structure-activity relationships for the pre-steady-state inhibition of cholesterol esterase by 4-nitrophenyl-N-substituted carbamates.Bioorg Med Chem. 2000 Nov;8(11):2601-7. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0896(00)00196-6. Bioorg Med Chem. 2000. PMID: 11092545
-
Molecular recognition by cholesterol esterase of active site ligands: structure-reactivity effects for inhibition by aryl carbamates and subsequent carbamylenzyme turnover.Biochemistry. 1996 Dec 24;35(51):16723-34. doi: 10.1021/bi961677v. Biochemistry. 1996. PMID: 8988009
Cited by
-
5,6-Benzoflavones as cholesterol esterase inhibitors: synthesis, biological evaluation and docking studies.Medchemcomm. 2018 Jan 19;9(3):490-502. doi: 10.1039/c7md00565b. eCollection 2018 Mar 1. Medchemcomm. 2018. PMID: 30108939 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hui DY. Molecular biology of enzymes involved with cholesterol esterase hydrolysis in mammalian tissues. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1996;1303:1–14. - PubMed
-
- Lopewz-Candales A, Bosner MS, Spilburg CA, Lange LG. Cholesterol transport function of pancreatic cholesterol esterase: directed sterol uptake and esterification in entercytes. Biochemistry. 1993;32:12085–12089. - PubMed
-
- Brockerhoff H, Jensen RG. Lipolytic enzymes. New York: Academic Press; 1974. Cholesterol esterase; pp. 176–193.
-
- Brodt-Eppley J, White P, Jenkins S, Hui D. Plasma cholesterol esterase level is a determinant for an atherogenic lipoprotein profile in normolipidemic human subjects. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1995;1272:69–72. - PubMed
-
- Chen JCH, Miercke LJW, Krucinski J, Starr JR, Saenz G, Wang X, Spilburg CA, Lange LG, Ellsworth JL, Stroud RM. Structure of bovine pancreatic cholesterol esterase at 1.6 Å: novel structural features involved in lipase activation. Biochemistry. 1998;37:5107–5117. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

