Ezetimibe blocks the internalization of NPC1L1 and cholesterol in mouse small intestine
- PMID: 22811412
- PMCID: PMC3435542
- DOI: 10.1194/jlr.M027359
Ezetimibe blocks the internalization of NPC1L1 and cholesterol in mouse small intestine
Abstract
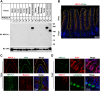
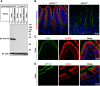
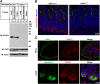
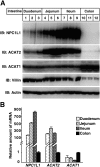
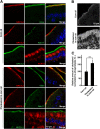
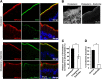
The multiple transmembrane protein Niemann-Pick C1 like1 (NPC1L1) is essential for intestinal cholesterol absorption. Ezetimibe binds to NPC1L1 and is a clinically used cholesterol absorption inhibitor. Recent studies in cultured cells have shown that NPC1L1 mediates cholesterol uptake through vesicular endocytosis that can be blocked by ezetimibe. However, how NPC1L1 and ezetimibe work in the small intestine is unknown. In this study, we found that NPC1L1 distributed in enterocytes of villi and transit-amplifying cells of crypts. Acyl-CoA cholesterol acyltransferase 2 (ACAT2), another important protein for cholesterol absorption by providing cholesteryl esters to chylomicrons, was mainly presented in the apical cytoplasm of enterocytes. NPC1L1 and ACAT2 were highly expressed in jejunum and ileum. ACAT1 presented in the Paneth cells of crypts and mesenchymal cells of villi. In the absence of cholesterol, NPC1L1 was localized on the brush border of enterocytes. Dietary cholesterol induced the internalization of NPC1L1 to the subapical layer beneath the brush border and became partially colocalized with the endosome marker Rab11. Ezetimibe blocked the internalization of NPC1L1 and cholesterol and caused their retention in the plasma membrane. This study demonstrates that NPC1L1 mediates cholesterol entering enterocytes through vesicular endocytosis and that ezetimibe blocks this step in vivo.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Multiple plasma membrane receptors but not NPC1L1 mediate high-affinity, ezetimibe-sensitive cholesterol uptake into the intestinal brush border membrane.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007 Sep;1771(9):1140-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2007.05.011. Epub 2007 Jun 23. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007. PMID: 17689140
-
Niemann-Pick C1 Like 1 protein is critical for intestinal cholesterol absorption.Science. 2004 Feb 20;303(5661):1201-4. doi: 10.1126/science.1093131. Science. 2004. PMID: 14976318
-
The cholesterol absorption inhibitor ezetimibe acts by blocking the sterol-induced internalization of NPC1L1.Cell Metab. 2008 Jun;7(6):508-19. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2008.04.001. Cell Metab. 2008. PMID: 18522832
-
NPC1L1 and cholesterol transport.FEBS Lett. 2010 Jul 2;584(13):2740-7. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2010.03.030. Epub 2010 Mar 19. FEBS Lett. 2010. PMID: 20307540 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ezetimibe blocks internalization of the NPC1L1/cholesterol complex.Cell Metab. 2008 Jun;7(6):469-71. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2008.05.001. Cell Metab. 2008. PMID: 18522826 Review.
Cited by
-
Exposure to dietary lipid leads to rapid production of cytosolic lipid droplets near the brush border membrane.Nutr Metab (Lond). 2016 Jul 28;13:48. doi: 10.1186/s12986-016-0107-9. eCollection 2016. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2016. PMID: 27478484 Free PMC article.
-
A Newly Integrated Model for Intestinal Cholesterol Absorption and Efflux Reappraises How Plant Sterol Intake Reduces Circulating Cholesterol Levels.Nutrients. 2019 Feb 1;11(2):310. doi: 10.3390/nu11020310. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 30717222 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cloning, phylogenetic analysis, tissue expression profiling, and functional roles of NPC1L1 in chickens, quails, and ducks.Poult Sci. 2025 May;104(5):105032. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2025.105032. Epub 2025 Mar 15. Poult Sci. 2025. PMID: 40106905 Free PMC article.
-
Polymorphisms of the Niemann-Pick C1-like 1 gene in a Japanese population.Biomed Rep. 2013 Jan;1(1):156-160. doi: 10.3892/br.2012.24. Epub 2012 Oct 17. Biomed Rep. 2013. PMID: 24648913 Free PMC article.
-
From Genetic Findings to new Intestinal Molecular Targets in Lipid Metabolism.Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2025 Jan 11;27(1):26. doi: 10.1007/s11883-024-01264-w. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2025. PMID: 39798054 Review.
References
-
- Wang D. Q. 2007. Regulation of intestinal cholesterol absorption. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 69: 221–248 - PubMed
-
- Burrier R. E., Smith A. A., McGregor D. G., Hoos L. M., Zilli D. L., Davis H. R., Jr 1995. The effect of acyl CoA: cholesterol acyltransferase inhibition on the uptake, esterification and secretion of cholesterol by the hamster small intestine. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 272: 156–163 - PubMed
-
- Buhman K. K., Accad M., Novak S., Choi R. S., Wong J. S., Hamilton R. L., Turley S., Farese R. V., Jr 2000. Resistance to diet-induced hypercholesterolemia and gallstone formation in ACAT2-deficient mice. Nat. Med. 6: 1341–1347 - PubMed
-
- Repa J. J., Buhman K. K., Farese R. V., Jr, Dietschy J. M., Turley S. D. 2004. ACAT2 deficiency limits cholesterol absorption in the cholesterol-fed mouse: impact on hepatic cholesterol homeostasis. Hepatology. 40: 1088–1097 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

