End-plate acetylcholine receptor: structure, mechanism, pharmacology, and disease
- PMID: 22811427
- PMCID: PMC3489064
- DOI: 10.1152/physrev.00015.2011
End-plate acetylcholine receptor: structure, mechanism, pharmacology, and disease
Abstract
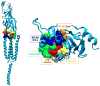
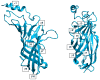
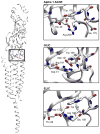
The synapse is a localized neurohumoral contact between a neuron and an effector cell and may be considered the quantum of fast intercellular communication. Analogously, the postsynaptic neurotransmitter receptor may be considered the quantum of fast chemical to electrical transduction. Our understanding of postsynaptic receptors began to develop about a hundred years ago with the demonstration that electrical stimulation of the vagus nerve released acetylcholine and slowed the heart beat. During the past 50 years, advances in understanding postsynaptic receptors increased at a rapid pace, owing largely to studies of the acetylcholine receptor (AChR) at the motor endplate. The endplate AChR belongs to a large superfamily of neurotransmitter receptors, called Cys-loop receptors, and has served as an exemplar receptor for probing fundamental structures and mechanisms that underlie fast synaptic transmission in the central and peripheral nervous systems. Recent studies provide an increasingly detailed picture of the structure of the AChR and the symphony of molecular motions that underpin its remarkably fast and efficient chemoelectrical transduction.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the author.
Figures
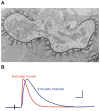
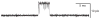
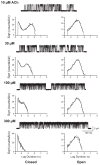
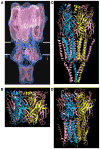
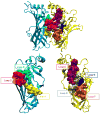










References
-
- Abraham SO, Scherf T, Eisenstein M, Chill JH, Anglister J. The mechanism for acetylcholine receptor inhibition by α-neurotoxins and species-specific resistance to α-bungarotoxin revealed by NMR. Neuron. 2002;35:319–332. - PubMed
-
- Abramson SN, Li Y, Culver P, Taylor P. An analog of lophotoxin reacts covalently with Tyr190 in the alpha-subunit of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989;264:12666–12672. - PubMed
-
- Adams PR. An analysis of the dose-response curve at voltage-clamped frog-endplates. Pflügers Arch. 1975;360:145–153. - PubMed
-
- Akabas MH, Kaufmann C, Archdeacon P, Karlin A. Identification of acetylcholine receptor channel-lining residues in the entire M2 segment of the alpha subunit. Neuron. 1994;13:919–927. - PubMed
-
- Akabas MH, Stauffer DA, Xu M, Karlin A. Acetylcholine receptor channel structure probed in cysteine-substitution mutants. Science. 1992;258:307–310. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

