Emerging role of non-coding RNA in neural plasticity, cognitive function, and neuropsychiatric disorders
- PMID: 22811697
- PMCID: PMC3395882
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2012.00132
Emerging role of non-coding RNA in neural plasticity, cognitive function, and neuropsychiatric disorders
Abstract
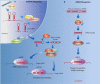
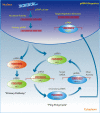
Non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) have emerged as critical regulators of transcription, epigenetic processes, and gene silencing, which make them ideal candidates for insight into molecular evolution and a better understanding of the molecular pathways of neuropsychiatric disease. Here, we provide an overview of the current state of knowledge regarding various classes of ncRNAs and their role in neural plasticity and cognitive function, and highlight the potential contribution they may make to the development of a variety of neuropsychiatric disorders, including schizophrenia, addiction, and fear-related anxiety disorders.
Keywords: addiction; anxiety; neuropsychiatric disorder; non-coding RNA.
Figures

References
-
- Aravin A., Gaidatzis D., Pfeffer S., Lagos-Quintana M., Landgraf P., Iovino N., Morris P., Brownstein M. J., Kuramochi-Miyagawa S., Nakano T., Chien M., Russo J. J., Ju J., Sheridan R., Sander C., Zavolan M., Tuschl T. (2006). A novel class of small RNAs bind to MILI protein in mouse testes. Nature 442 203–207 - PubMed
-
- Aravin A. A., Hannon G. J., Brennecke J. (2007). The Piwi-piRNA pathway provides an adaptive defense in the transposon arms race. Science 318 761–764 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

