The Impact of Macrophage Nucleotide Pools on HIV-1 Reverse Transcription, Viral Replication, and the Development of Novel Antiviral Agents
- PMID: 22811909
- PMCID: PMC3395185
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/625983
The Impact of Macrophage Nucleotide Pools on HIV-1 Reverse Transcription, Viral Replication, and the Development of Novel Antiviral Agents
Abstract
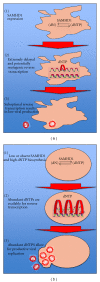
Macrophages are ubiquitous and represent a significant viral reservoir for HIV-1. Macrophages are nondividing, terminally differentiated cells, which have a unique cellular microenvironment relative to actively dividing T lymphocytes, all of which can impact HIV-1 infection/replication, design of inhibitors targeting viral replication in these cells, emergence of mutations within the HIV-1 genome, and disease progression. Scarce dNTPs drive rNTP incorporation into the proviral DNA in macrophages but not lymphocytes. Furthermore, the efficacy of a ribose-based inhibitor that potently inhibits HIV-1 replication in macrophages, has prompted a reconsideration of the previously accepted dogma that 2'-deoxy-based inhibitors demonstrate effective inhibition of HIV-1 replication. Additionally, higher levels of dUTP and rNTP incorporation in macrophages, and lack of repair mechanisms relative to lymphocytes, provide a further mechanistic understanding required to develop targeted inhibition of viral replication in macrophages. Together, the concentrations of dNTPs and rNTPs within macrophages comprise a distinctive cellular environment that directly impacts HIV-1 replication in macrophages and provides unique insight into novel therapeutic mechanisms that could be exploited to eliminate virus from these cells.
Figures

References
-
- Alkhatib G, Combadiere C, Broder CC, et al. CC CKR5: a RANTES, MIP-1α, MIP-1β receptor as a fusion cofactor for macrophage-tropic HIV-1. Science. 1996;272(5270):1955–1958. - PubMed
-
- Aquaro S, Bagnarelli P, Guenci T, et al. Long-term survival and virus production in human primary macrophages infected by human immunodeficiency virus. Journal of Medical Virology. 2002;68(4):479–488. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
