Transmetatarsal amputation: a case series and review of the literature
- PMID: 22811912
- PMCID: PMC3397208
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/797218
Transmetatarsal amputation: a case series and review of the literature
Abstract
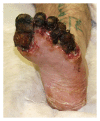
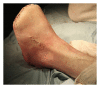
Foot ulceration is a major cause of morbidity amongst patients with diabetes. In severe cases of ulceration, osteomyelitis and amputation can ensue. A distinct lack of agreement exists on the most appropriate level of amputation in cases of severe foot ulceration/infection to provide predictable healing rates. This paper provides an overview of the transmetatarsal amputation (TMA) as a limb salvage procedure and is written with the perspective and experiences of the Department of Podiatric Surgery at West Middlesex University Hospital (WMUH). We have reflected on the cases of 11 patients (12 feet) and have found the TMA to be an effective procedure in the management of cases of severe forefoot ulceration and infection.
Figures
References
-
- Eldor R, Raz I, Yehuda AB, Boulton AJM. New and experimental approaches to treatment of diabetic foot ulcers: a comprehensive review of emerging treatment strategies. Diabetic Medicine. 2004;21(11):1161–1173. - PubMed
-
- Ramsey SD, Newton K, Blough D, et al. Incidence, outcomes, and cost of foot ulcers in patients with diabetes. Diabetes Care. 1999;22(3):382–387. - PubMed
-
- Bates MC, AbuRahma AF. An update on endovascular therapy of the lower extremities. Journal of Endovascular Therapy. 2004;11(2, supplement):II107–II127. - PubMed
-
- Boulton AJM. The diabetic foot. Medicine. 2006;34(3):87–90.
-
- Hartemann-Heurtier A, Senneville E. Diabetic foot osteomyelitis. Diabetes and Metabolism. 2008;34(2):87–95. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical