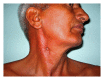
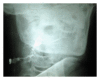
Unusual cause of orocutaneous fistula in the neck
- PMID: 22811946
- PMCID: PMC3395166
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/658536
Unusual cause of orocutaneous fistula in the neck
Abstract
A case of orocutaneous fistula secondary to submandibular sialolithiasis, which was masquerading clinically as branchial fistula is presented. This case highlights the importance of conducting fistulogram in the evaluation of discharging lesions in the neck.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[A Contrivance for Closure and Dressing of Orocutaneous Fistula Developed in Advanced Oral Cancer].Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 2017 Nov;44(12):1287-1289. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho. 2017. PMID: 29394609 Japanese.
-
Complete branchial fistula. Case report and review of the literature.Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2001 Nov;110(11):1077-9. doi: 10.1177/000348940111001116. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2001. PMID: 11713922 Review.
-
Chronic sialadenitis with sialolithiasis associated with parapharyngeal fistula and tonsillolith.Radiol Case Rep. 2017 Jul 10;12(3):519-522. doi: 10.1016/j.radcr.2017.06.002. eCollection 2017 Sep. Radiol Case Rep. 2017. PMID: 28828116 Free PMC article.
-
Congenital Orocutaneous Fistula Associated With Ectopic Salivary Glands and Submandibular Gland Aplasia.Laryngoscope. 2021 Mar;131(3):E998-E1001. doi: 10.1002/lary.28921. Epub 2020 Jul 10. Laryngoscope. 2021. PMID: 33059385 No abstract available.
-
Unusual coexistence of first and second branchial fistulas: clinical case and review of the literature.J Int Med Res. 2020 Aug;48(8):300060520944303. doi: 10.1177/0300060520944303. J Int Med Res. 2020. PMID: 32865080 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Early Clinical Mapping of Submandibular Gland Fistula: A Case Report and Systematic Review.Int Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2023 Oct 6;28(3):e537-e542. doi: 10.1055/s-0043-1767801. eCollection 2024 Jul. Int Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2023. PMID: 38974643 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bilateral Orocutaneous Fistula Secondary to Pericoronal Infection of Mandibular Third Molars: A Rare Case Report.Clin Case Rep. 2025 Jan 14;13(1):e70017. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.70017. eCollection 2025 Jan. Clin Case Rep. 2025. PMID: 39816707 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wilson SW, Ward DJ, Burns A. Dental infections masquerading as skin lesions. British Journal of Plastic Surgery. 2001;54(4):358–360. - PubMed
-
- Drage NA, Brown JE, Makdissi J, Townend J. Migrating salivary stones: report of three cases. British Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery. 2005;43(2):180–182. - PubMed
-
- Ang AHC, Pang KP, Tan LKS. Complete branchial fistula: case report and review of the literature. Annals of Otology, Rhinology and Laryngology. 2001;110(11):1077–1079. - PubMed
-
- Baskota DK, Prasad R, Sinha BK, Amatya RCM. Frequency and effective treatment of ulcers and sinuses in cases of tuberculous cervical lymphadenitis. Journal of the College of Physicians and Surgeons Pakistan. 2005;15(3):157–159. - PubMed
-
- Asfar SK, Steitiyeh MR, Abdul-Amir R. Giant salivary calculi: an orocervical fistula caused by a submandibular gland calculus. Canadian Journal of Surgery. 1989;32(4):295–296. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources