Synthesis and evaluation of a peptide targeted small molecular Gd-DOTA monoamide conjugate for MR molecular imaging of prostate cancer
- PMID: 22812444
- PMCID: PMC3552558
- DOI: 10.1021/bc300009t
Synthesis and evaluation of a peptide targeted small molecular Gd-DOTA monoamide conjugate for MR molecular imaging of prostate cancer
Abstract
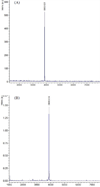
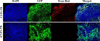
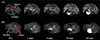
Tumor extracellular matrix has an abundance of cancer related proteins that can be used as biomarkers for cancer molecular imaging. Innovative design and development of safe and effective targeted contrast agents to these biomarkers would allow effective MR cancer molecular imaging with high spatial resolution. In this study, we synthesized a low molecular weight CLT1 peptide targeted Gd(III) chelate CLT1-dL-(Gd-DOTA)(4) specific to clotted plasma proteins in tumor stroma for cancer MR molecular imaging. CLT1-dL-(Gd-DOTA)(4) was synthesized by conjugating four Gd-DOTA monoamide chelates to a CLT1 peptide via generation 1 lysine dendrimer. The T(1) relaxivity of CLT1-dL-(Gd-DOTA)(4) was 40.4 mM(-1) s(-1) per molecule (10.1 mM(-1) s(-1) per Gd) at 37 °C and 1.5 T. Fluorescence imaging showed high binding specificity of CLT1 to orthotopic PC3 prostate tumor in mice. The contrast agent resulted in improved tumor contrast enhancement in male athymic nude mice bearing orthotopic PC3 prostate tumor xenograft at a dose of 0.03 mmol Gd/kg. The peptide targeted MRI contrast agent is promising for high-resolution MR molecular imaging of prostate tumor.
Figures


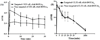


References
-
- Vlastos G, Verkooijen HM. Minimally invasive approaches for diagnosis and treatment of early-stage breast cancer. Oncologist. 2007;12:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Gelovani JG. Molecular imaging of epidermal growth factor receptor expression-activity at the kinase level in tumors with positron emission tomography. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2008;27:645–653. - PubMed
-
- Piwnica-Worms D, Kesarwala AH, Pichler A, Prior JL, Sharma V. Single photon emission computed tomography and positron emission tomography imaging of multi-drug resistant P-glycoprotein--monitoring a transport activity important in cancer, blood-brain barrier function and Alzheimer's disease. Neuroimaging Clin N Am. 2006;16:575–589. - PubMed
-
- Hayashi M, Murakami K, Oyama T, Domeki Y, Hagiwara S, Katsumata D, Sunagawa M. PET/CT supports breast cancer diagnosis and treatment. Breast Cancer. 2008;15:224–230. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

