Increased gray matter volume in the right angular and posterior parahippocampal gyri in loving-kindness meditators
- PMID: 22814662
- PMCID: PMC3541494
- DOI: 10.1093/scan/nss076
Increased gray matter volume in the right angular and posterior parahippocampal gyri in loving-kindness meditators
Abstract
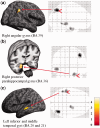
Previous voxel-based morphometry (VBM) studies have revealed that meditation is associated with structural brain changes in regions underlying cognitive processes that are required for attention or mindfulness during meditation. This VBM study examined brain changes related to the practice of an emotion-oriented meditation: loving-kindness meditation (LKM). A 3 T magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scanner captured images of the brain structures of 25 men, 10 of whom had practiced LKM in the Theravada tradition for at least 5 years. Compared with novices, more gray matter volume was detected in the right angular and posterior parahippocampal gyri in LKM experts. The right angular gyrus has not been previously reported to have structural differences associated with meditation, and its specific role in mind and cognitive empathy theory suggests the uniqueness of this finding for LKM practice. These regions are important for affective regulation associated with empathic response, anxiety and mood. At the same time, gray matter volume in the left temporal lobe in the LKM experts appeared to be greater, an observation that has also been reported in previous MRI meditation studies on meditation styles other than LKM. Overall, the findings of our study suggest that experience in LKM may influence brain structures associated with affective regulation.
Figures
References
-
- Ashburner J. A fast diffeomorphic image registration algorithm. NeuroImage. 2007;38:95–113. - PubMed
-
- Ashburner J, Friston KJ. Voxel-based morphometry—the methods. NeuroImage. 2000;11:805–21. - PubMed
-
- Bergouignan L, Chupin M, Czechowska Y, et al. Can voxel based morphometry, manual segmentation and automated segmentation equally detect hippocampal volume differences in acute depression? NeuroImage. 2009;45:29–37. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

