Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) plasma levels at oocyte retrieval and IVF outcomes
- PMID: 22815004
- PMCID: PMC3492576
- DOI: 10.1007/s10815-012-9826-7
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) plasma levels at oocyte retrieval and IVF outcomes
Abstract
Purpose: The aim of our study was to ascertain the influence of hCG levels at oocyte pick-up on IVF outcomes, and their relationship with clinical parameters.
Methods: A prospective study was performed including 473 women undergoing IVF, aged under 40 years. Blood samples to analyze hCG levels were obtained at the time of follicular aspiration, 36 h after the administration of 250 μg of recombinant hCG.
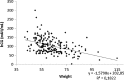
Results: Neither the numbers of oocytes obtained or fertilized, nor the pregnancy rate, were correlated with hCG levels. Moreover, hCG values were very similar in women who did and did not become pregnant (123.3 ± 48.7 and 117.5 ± 44.7 mUI/mL). Cases in which no oocytes were recovered after follicular aspiration had similar hCG levels to those in which more than 1 oocyte was obtained. On the other hand, hCG levels were negatively related to body mass index, weight, and age.
Conclusions: These data indicate that after the administration of 250 μg of recombinant hCG, hCG levels are not responsible for failure to recover oocytes. Specifically, there was no correlation between plasma hCG levels and the number of oocytes obtained or other markers of IVF outcome. There was, however, an inverse relationship with BMI, body weight and age.
Figures
References
-
- Driscoll GL, Tyler JPP, Hangan JT, et al. A prospective, randomized, controlled, double-blind, double-dummy comparison of recombinant and urinary HCG for inducing oocyte maturation and follicular luteinization in ovarian stimulation. Hum Reprod. 2000;15:1305–10. doi: 10.1093/humrep/15.6.1305. - DOI - PubMed
-
- European Recombinant Human Chorionic Gonadotrophin Study Group Induction of final follicular maturation and early luteinization in women undergoing ovulation induction for assisted reproduction treatment: recombinant HCG versus urinary HCG. Hum Reprod. 2000;15:1446–551. doi: 10.1093/humrep/15.7.1446. - DOI - PubMed
-
- International Recombinant Human Chorionic Gonadotropin Study Group Induction of ovulation in World Health Organization group II anovulatory women undergoing follicular stimulation with recombinant human follicle-stimulating hormone: a comparison of recombinant human chorionic gonadotropin (rhCG) and urinary hCG. Fertil Steril. 2001;75:1111–8. doi: 10.1016/S0015-0282(01)01803-9. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chang P, Kenley S, Burns T, et al. Multicenter Study 7929 Investigator Group. Recombinant human chorionic gonadotropin (rhCG) in assisted reproductive technology: results of a clinical trial comparing two doses of rhCG (Ovidrel®) to urinary hCG (Profasi®) for induction of final follicular maturation in in vitro fertilization-embryo transfer. Fertil Steril. 2001;76:67–74. doi: 10.1016/S0015-0282(01)01851-9. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources