Two types of laminolysis in adolescent athletes
- PMID: 22815057
- PMCID: PMC3506832
- DOI: 10.1007/s10195-012-0206-y
Two types of laminolysis in adolescent athletes
Abstract
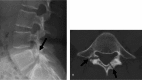
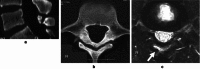
Bony defects in the spine are divided into three main types: spondylolysis, pediculolysis, and laminolysis. Lumbar spondylolysis is a well-known stress fracture that occurs frequently in adolescent athletes. Pediculolysis means stress fracture of the pedicle, which sometimes occurs subsequent to unilateral spondylolysis. Laminolysis is a rarely reported stress fracture similar to spondylolysis and pediculolysis that sometimes causes low back pain (LBP). However, its pathomechanism has not been elucidated. Recently, we encountered four adolescent athletes with symptomatic laminolysis. Mean age was 15.8 (range 15-17) years. All subjects reported severe LBP exacerbated by extension of the lumbar spine, and radiology revealed two types of laminolysis: hemilaminar type and intralaminar type. To elucidate the mechanisms of each type, we reviewed a biomechanical study, and found that the hemilaminar type was thought to be subsequent to contralateral spondylolysis, while the intralaminar type might be a result of a stress fracture due to repetitive extension loading.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Spontaneous multilevel lumbar pediculolysis associated with spondylolysis: a rare case and review of the literature.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024 Nov 21;25(1):936. doi: 10.1186/s12891-024-08084-8. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024. PMID: 39574019 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adolescents with symptomatic laminolysis: report of two cases.J Orthop Traumatol. 2010 Sep;11(3):189-93. doi: 10.1007/s10195-010-0101-3. Epub 2010 Aug 19. J Orthop Traumatol. 2010. PMID: 20721597 Free PMC article.
-
Athletes with unilateral spondylolysis are at risk of stress fracture at the contralateral pedicle and pars interarticularis: a clinical and biomechanical study.Am J Sports Med. 2005 Apr;33(4):583-90. doi: 10.1177/0363546504269035. Epub 2005 Feb 8. Am J Sports Med. 2005. PMID: 15722292
-
Pars Interarticularis and Pedicle Stress Injuries in Young Athletes With Low Back Pain: A Retrospective Cohort Study of 902 Patients Evaluated With Magnetic Resonance Imaging.Am J Sports Med. 2024 Aug;52(10):2639-2645. doi: 10.1177/03635465241264804. Epub 2024 Aug 11. Am J Sports Med. 2024. PMID: 39129296
-
[Research progress of stress fracture of lumbar pedicle].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2013 Feb;27(2):240-2. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 23596697 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Symptomatic Unilateral Spondylolysis Associated With Nonspondylolytic Lateral Clefts in Adults: Review of an Infrequently Reported Pathology.Cureus. 2016 Dec 12;8(12):e928. doi: 10.7759/cureus.928. Cureus. 2016. PMID: 28097079 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spontaneous multilevel lumbar pediculolysis associated with spondylolysis: a rare case and review of the literature.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024 Nov 21;25(1):936. doi: 10.1186/s12891-024-08084-8. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2024. PMID: 39574019 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-traumatic lumbar spondylolysis with contralateral pedicle and lamina fracture: a case report and review of the literature.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2025 Jan 14;26(1):48. doi: 10.1186/s12891-025-08293-9. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2025. PMID: 39810096 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-Isthmic Spondylolysis Imaging Features: A Case Report.J Orthop Case Rep. 2022 Feb;12(2):42-44. doi: 10.13107/jocr.2022.v12.i02.2658. J Orthop Case Rep. 2022. PMID: 36199724 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging Features of Non-Isthmic Spondylolysis: A Case Report.Spine Surg Relat Res. 2019 Nov 1;4(2):187-189. doi: 10.22603/ssrr.2019-0054. eCollection 2020. Spine Surg Relat Res. 2019. PMID: 32405568 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Sairyo K, Katoh S, Sakamaki T, Komatsubara S, Endo K, Yasui N. Three successive stress fractures at the same level in an adolescent baseball player. Am J Sports Med. 2003;31:606–610. - PubMed
-
- Wiltse LL. The etiology of spondylolisthesis. J Bone Joint Surg. 1962;44-A:539–560. - PubMed
-
- Fredrickson BE, Baker D, McHolick WJ, Yuan HA, Lubicky JP. The natural history of spondylolysis and spondylolisthesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1984;66:699–707. - PubMed
-
- Sairyo K, Katoh S, Sasa T, Yasui N, Goel VK, Vadapalli S, et al. Athletes with unilateral spondylolysis are at risk of stress fracture at the contralateral pedicle and pars interarticularis: a clinical and biomechanical study. Am J Sports Med. 2005;33(4):583–590. doi: 10.1177/0363546504269035. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

