A peculiar cause of anaphylaxis: no more steak? The journey to discovery of a newly recognized allergy to galactose-alpha-1,3-galactose found in mammalian meat
- PMID: 22815061
- PMCID: PMC3614139
- DOI: 10.1007/s11606-012-2144-z
A peculiar cause of anaphylaxis: no more steak? The journey to discovery of a newly recognized allergy to galactose-alpha-1,3-galactose found in mammalian meat
Abstract
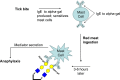
In recent years, a newly recognized allergic disease has been uncovered, and seemingly idiopathic causes of anaphylaxis now have an explanation. Individuals bitten by the lone star tick may develop IgE antibodies to the carbohydrate galactose-α-1,3-galactose (alpha-gal). Upon exposure of sensitized subjects to mammalian meat containing alpha-gal on glycoproteins or glycolipids, delayed anaphylaxis may ensue, often three to six hours after ingestion.1 Many of these individuals have negative allergy skin prick tests to meat, further obscuring the diagnosis. With the recent development of IgE alpha-gal tests, the clinical diagnosis can be confirmed in the laboratory.
Figures

References
-
- Commins SP, Satinover SM, Hosen J, Mozena J, Borish L, Lewis BD, et al. Delayed anaphylaxis, angioedema, or urticaria after consumption of red meat in patients with IgE antibodies specific for galactose-alpha-1,3-galactose. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009;123(2):426–33. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2008.10.052. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Commins SP, James HR, Kelly LA, Pochan SL, Workman LJ, Perzanowski MS, et al. The relevance of tick bites to the production of IgE antibodies to the mammalian oligosaccharide galactose-alpha-1,3-galactose. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011;127(5):1286,93.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2011.02.019. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Qian J, Liu T, Yang L, Daus A, Crowley R, Zhou Q. Structural characterization of N-linked oligosaccharides on monoclonal antibody cetuximab by the combination of orthogonal matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization hybrid quadrupole-quadrupole time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry and sequential enzymatic digestion. Anal Biochem. 2007;364(1):8–18. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2007.01.023. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

