Endogenous inhibitor proteins that connect Ser/Thr kinases and phosphatases in cell signaling
- PMID: 22815089
- PMCID: PMC3422418
- DOI: 10.1002/iub.1067
Endogenous inhibitor proteins that connect Ser/Thr kinases and phosphatases in cell signaling
Abstract
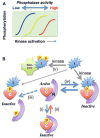
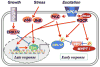
Protein phosphatase activity acts as a primary determinant of the extent and duration of phosphorylation of cellular proteins in response to physiological stimuli. Ser/Thr protein phosphatase-1 (PP1) belongs to the PPP superfamily, and is associated with regulatory subunits that confer substrate specificity, allosteric regulation, and subcellular compartmentalization. In addition, all eukaryotic cells contain multiple heat-stable proteins that originally were thought to inhibit phosphatase catalytic subunits released from the regulatory subunits, as a fail-safe mechanism. However, discovery of C-kinase-activated PP1 inhibitor, Mr of 17 kDa (CPI-17) required fresh thinking about the endogenous inhibitors as specific regulators of particular phosphatase complexes, acting in addition to, not instead of, regulatory subunits. The cellular actions of the endogenous inhibitors are controlled by phosphorylation, connecting them to kinase pathways. More recent progress has unveiled additional functions of PP1 inhibitor-2 (I-2), including regulation of protein kinases. Transcriptional mechanisms govern the expression levels of CPI-17 in response to stimuli. If true for other inhibitor proteins, they have the potential of being diagnostic markers for pathological conditions. We discuss specific examples of PP1 inhibitor proteins regulating particular cellular functions and the rationale for incorporating phosphatase inhibitor proteins in development of new therapeutic strategies.
Copyright © 2012 International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Regulation of cellular protein phosphatase-1 (PP1) by phosphorylation of the CPI-17 family, C-kinase-activated PP1 inhibitors.J Biol Chem. 2009 Dec 18;284(51):35273-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R109.059972. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19846560 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The inhibitor-1 C terminus facilitates hormonal regulation of cellular protein phosphatase-1: functional implications for inhibitor-1 isoforms.J Biol Chem. 2004 Nov 19;279(47):48904-14. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M404416200. Epub 2004 Sep 2. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15345721
-
EmbR, a regulatory protein with ATPase activity, is a substrate of multiple serine/threonine kinases and phosphatase in Mycobacterium tuberculosis.FEBS J. 2006 Jun;273(12):2711-21. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2006.05289.x. FEBS J. 2006. PMID: 16817899
-
Structural basis of protein phosphatase 1 regulation.Nature. 2004 Jun 17;429(6993):780-4. doi: 10.1038/nature02582. Epub 2004 May 26. Nature. 2004. PMID: 15164081
-
From promiscuity to precision: protein phosphatases get a makeover.Mol Cell. 2009 Mar 13;33(5):537-45. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.02.015. Mol Cell. 2009. PMID: 19285938 Review.
Cited by
-
PHI-1, an Endogenous Inhibitor Protein for Protein Phosphatase-1 and a Pan-Cancer Marker, Regulates Raf-1 Proteostasis.Biomolecules. 2023 Dec 4;13(12):1741. doi: 10.3390/biom13121741. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 38136612 Free PMC article.
-
TIMAP inhibits endothelial myosin light chain phosphatase by competing with MYPT1 for the catalytic protein phosphatase 1 subunit PP1cβ.J Biol Chem. 2019 Sep 6;294(36):13280-13291. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.006075. Epub 2019 Jul 17. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 31315927 Free PMC article.
-
Expressions of the Protein Phosphatases PP1 and PP4 during the Embryonic Diapause Process of the Silkworm Bombyx mori.Zool Stud. 2022 Nov 29;61:e61. doi: 10.6620/ZS.2022.61-61. eCollection 2022. Zool Stud. 2022. PMID: 37007811 Free PMC article.
-
Possible roles of N- and C-terminal unstructured tails of CPI-17 in regulating Ca2+ sensitization force of smooth muscle.J Smooth Muscle Res. 2022;58(0):22-33. doi: 10.1540/jsmr.58.22. J Smooth Muscle Res. 2022. PMID: 35418530 Free PMC article.
-
Structure, regulation, and mechanisms of nonmuscle myosin-2.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024 Jun 15;81(1):263. doi: 10.1007/s00018-024-05264-6. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 38878079 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Brautigan DL. Protein Ser/Thr Phosphatases : The Ugly Ducklings of Cell Signaling. FEBS J 2012 - PubMed
-
- Gharbi-Ayachi A, Labbé J, Burgess A, Vigneron S, Strub J, Brioudes E, et al. The substrate of Greatwall kinase, Arpp19, controls mitosis by inhibiting protein phosphatase 2A. Science. 2010;330:1673–1677. - PubMed
-
- Mochida S, Maslen SL, Skehel M, Hunt T. Greatwall phosphorylates an inhibitor of protein phosphatase 2A that is essential for mitosis. Science. 2010;330:1670–1673. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

