Inhibition of rhabdomyosarcoma cell and tumor growth by targeting specificity protein (Sp) transcription factors
- PMID: 22815231
- PMCID: PMC3527649
- DOI: 10.1002/ijc.27730
Inhibition of rhabdomyosarcoma cell and tumor growth by targeting specificity protein (Sp) transcription factors
Erratum in
-
Erratum: inhibition of rhabdomyosarcoma cell and tumor growth by targeting specificity protein (sp) transcription factors.Int J Cancer. 2015 Sep 15;137(6):E9. doi: 10.1002/ijc.29551. Int J Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26153648 No abstract available.
Abstract
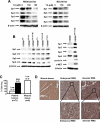
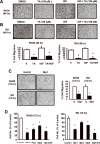
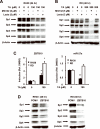
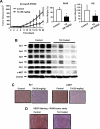
Specificity protein (Sp) transcription factors Sp1, Sp3 and Sp4 are highly expressed in rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) cells. In tissue arrays of RMS tumor cores from 71 patients, 80% of RMS patients expressed high levels of Sp1 protein, whereas low expression of Sp1 was detected in normal muscle tissue. The non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) tolfenamic acid (TA) inhibited growth and migration of RD and RH30 RMS cell lines and also inhibited tumor growth in vivo using a mouse xenograft (RH30 cells) model. The effects of TA were accompanied by downregulation of Sp1, Sp3, Sp4 and Sp-regulated genes in RMS cells and tumors, and the role of Sp protein downregulation in mediating inhibition of RD and RH30 cell growth and migration was confirmed by individual and combined knockdown of Sp1, Sp3 and Sp4 proteins by RNA interference. TA treatment and Sp knockdown in RD and RH30 cells also showed that four genes that are emerging as individual drug targets for treating RMS, namely c-MET, insulin-like growth factor receptor (IGFR), PDGFRα and CXCR4, are also Sp-regulated genes. These results suggest that NSAIDs such as TA may have potential clinical efficacy in drug combinations for treating RMS patients.
Copyright © 2012 UICC.
Figures


References
-
- Paulino AC, Okcu MF. Rhabdomyosarcoma. Curr Probl Cancer. 2008;32:7–34. - PubMed
-
- Ries LAG, Smith MA, Gurney JG, Linet M, Tamra T, Young JL, Bunin GR. Cancer Incidence and Survival Among Children and Adolescents: United States SEER Program 1975-1995. NIH Pub. No. 99-4649 National Institutes of Health; 1999.
-
- Grufferman S, Schwartz AG, Ruymann FB, Maurer HM. Parents’ use of cocaine and marijuana and increased risk of rhabdomyosarcoma in their children. Cancer Causes Control. 1993;4:217–24. - PubMed
-
- Hicks N, Zack M, Caldwell GG, Fernbach DJ, Falletta JM. Childhood cancer and occupational radiation exposure in parents. Cancer. 1984;53:1637–43. - PubMed
-
- Barr FG, Galili N, Holick J, Biegel JA, Rovera G, Emanuel BS. Rearrangement of the PAX3 paired box gene in the paediatric solid tumour alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma. Nat Genet. 1993;3:113–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

