Structural insights into the anti-methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) activity of ceftobiprole
- PMID: 22815485
- PMCID: PMC3442540
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.355644
Structural insights into the anti-methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) activity of ceftobiprole
Abstract
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) is an antibiotic-resistant strain of S. aureus afflicting hospitals and communities worldwide. Of greatest concern is its development of resistance to current last-line-of-defense antibiotics; new therapeutics are urgently needed to combat this pathogen. Ceftobiprole is a recently developed, latest generation cephalosporin and has been the first to show activity against MRSA by inhibiting essential peptidoglycan transpeptidases, including the β-lactam resistance determinant PBP2a, from MRSA. Here we present the structure of the complex of ceftobiprole bound to PBP2a. This structure provides the first look at the molecular details of an effective β-lactam-resistant PBP interaction, leading to new insights into the mechanism of ceftobiprole efficacy against MRSA.
Figures
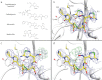

References
-
- Neu H. C. (1992) The crisis in antibiotic resistance. Science 257, 1064–1073 - PubMed
-
- Barrett F. F., McGehee R. F., Jr., Finland M. (1968) Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus at Boston City Hospital: bacteriologic and epidemiologic observations. New Engl. J. Med. 279, 441–448 - PubMed
-
- Doshi R. K., Patel G., Mackay R., Wallach F. (2009) Healthcare-associated infections: epidemiology, prevention, and therapy. Mt. Sinai J. Med. 76, 84–94 - PubMed
-
- Sievert D. M., Rudrik J. T., Patel J. B., McDonald L. C., Wilkins M. J., Hageman J. C. (2008) Vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in the United States, 2002–2006. Clin. Infect. Dis. 46, 668–674 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

