I(A) channels encoded by Kv1.4 and Kv4.2 regulate neuronal firing in the suprachiasmatic nucleus and circadian rhythms in locomotor activity
- PMID: 22815518
- PMCID: PMC3752070
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0174-12.2012
I(A) channels encoded by Kv1.4 and Kv4.2 regulate neuronal firing in the suprachiasmatic nucleus and circadian rhythms in locomotor activity
Abstract
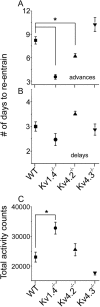
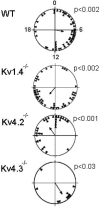
Neurons in the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) display coordinated circadian changes in electrical activity that are critical for daily rhythms in physiology, metabolism, and behavior. SCN neurons depolarize spontaneously and fire repetitively during the day and hyperpolarize, drastically reducing firing rates, at night. To explore the hypothesis that rapidly activating and inactivating A-type (I(A)) voltage-gated K(+) (Kv) channels, which are also active at subthreshold membrane potentials, are critical regulators of the excitability of SCN neurons, we examined locomotor activity and SCN firing in mice lacking Kv1.4 (Kv1.4(-/-)), Kv4.2 (Kv4.2(-/-)), or Kv4.3 (Kv4.3(-/-)), the pore-forming (α) subunits of I(A) channels. Mice lacking either Kv1.4 or Kv4.2 α subunits have markedly shorter (0.5 h) periods of locomotor activity than wild-type (WT) mice. In vitro extracellular multi-electrode recordings revealed that Kv1.4(-/-) and Kv4.2(-/-) SCN neurons display circadian rhythms in repetitive firing, but with shorter periods (0.5 h) than WT cells. In contrast, the periods of wheel-running activity in Kv4.3(-/-) mice and firing in Kv4.3(-/-) SCN neurons were indistinguishable from WT animals and neurons. Quantitative real-time PCR revealed that the transcripts encoding all three Kv channel α subunits, Kv1.4, Kv4.2, and Kv4.3, are expressed constitutively throughout the day and night in the SCN. Together, these results demonstrate that Kv1.4- and Kv4.2-encoded I(A) channels regulate the intrinsic excitability of SCN neurons during the day and night and determine the period and amplitude of circadian rhythms in SCN neuron firing and locomotor behavior.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Acute Knockdown of Kv4.1 Regulates Repetitive Firing Rates and Clock Gene Expression in the Suprachiasmatic Nucleus and Daily Rhythms in Locomotor Behavior.eNeuro. 2017 May 23;4(3):ENEURO.0377-16.2017. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0377-16.2017. eCollection 2017 May-Jun. eNeuro. 2017. PMID: 28560311 Free PMC article.
-
IA Channels Encoded by Kv1.4 and Kv4.2 Regulate Circadian Period of PER2 Expression in the Suprachiasmatic Nucleus.J Biol Rhythms. 2015 Oct;30(5):396-407. doi: 10.1177/0748730415593377. Epub 2015 Jul 6. J Biol Rhythms. 2015. PMID: 26152125 Free PMC article.
-
A-type K+ channels encoded by Kv4.2, Kv4.3 and Kv1.4 differentially regulate intrinsic excitability of cortical pyramidal neurons.J Physiol. 2012 Aug 15;590(16):3877-90. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2012.229013. Epub 2012 May 21. J Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22615428 Free PMC article.
-
Ion Channels Controlling Circadian Rhythms in Suprachiasmatic Nucleus Excitability.Physiol Rev. 2020 Oct 1;100(4):1415-1454. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00027.2019. Epub 2020 Mar 12. Physiol Rev. 2020. PMID: 32163720 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Linking neural activity and molecular oscillations in the SCN.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2011 Sep 2;12(10):553-69. doi: 10.1038/nrn3086. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21886186 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neuroinflammation and oxidative stress in rostral ventrolateral medulla contribute to neurogenic hypertension induced by systemic inflammation.J Neuroinflammation. 2012 Sep 7;9:212. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-9-212. J Neuroinflammation. 2012. PMID: 22958438 Free PMC article.
-
Control of Sleep Onset by Shal/Kv4 Channels in Drosophila Circadian Neurons.J Neurosci. 2018 Oct 17;38(42):9059-9071. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0777-18.2018. Epub 2018 Sep 5. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30185460 Free PMC article.
-
Kv12-Encoded K + Channels Drive the Day-Night Switch in the Repetitive Firing Rates of SCN Neurons.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Feb 2:2023.01.30.526323. doi: 10.1101/2023.01.30.526323. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: J Gen Physiol. 2023 Sep 4;155(9):e202213310. doi: 10.1085/jgp.202213310. PMID: 36778242 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Acute Knockdown of Kv4.1 Regulates Repetitive Firing Rates and Clock Gene Expression in the Suprachiasmatic Nucleus and Daily Rhythms in Locomotor Behavior.eNeuro. 2017 May 23;4(3):ENEURO.0377-16.2017. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0377-16.2017. eCollection 2017 May-Jun. eNeuro. 2017. PMID: 28560311 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct Firing Properties of Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide-Expressing Neurons in the Suprachiasmatic Nucleus.J Biol Rhythms. 2016 Feb;31(1):57-67. doi: 10.1177/0748730415619745. Epub 2015 Dec 27. J Biol Rhythms. 2016. PMID: 26712166 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albus H, Bonnefont X, Chaves I, Yasui A, Doczy J, van der Horst GT, Meijer JH. Cryptochrome-deficient mice lack circadian electrical activity in the suprachiasmatic nuclei. Curr Biol. 2002;12:1130–1133. - PubMed
-
- Batschelet E, Sibson R, Cohen JE. Circular statistics in biology. In: Sibson R, Cohen JE, editors. Mathematics in biology. New York: Academic; 1981. pp. 31–54.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
