Role of heat-stable enterotoxins in the induction of early immune responses in piglets after infection with enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli
- PMID: 22815904
- PMCID: PMC3398878
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0041041
Role of heat-stable enterotoxins in the induction of early immune responses in piglets after infection with enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli
Abstract
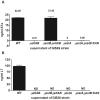
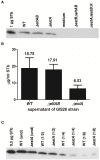
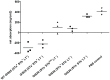
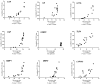
Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) strains that produce heat-stable (ST) and/or heat-labile (LT) enterotoxins are cause of post-weaning diarrhea in piglets. However, the relative importance of the different enterotoxins in host immune responses against ETEC infection has been poorly defined. In the present study, several isogenic mutant strains of an O149:F4ac(+), LT(+) STa(+) STb(+) ETEC strain were constructed that lack the expression of LT in combination with one or both types of ST enterotoxins (STa and/or STb). The small intestinal segment perfusion (SISP) technique and microarray analysis were used to study host early immune responses induced by these mutant strains 4 h after infection in comparison to the wild type strain and a PBS control. Simultaneously, net fluid absorption of pig small intestinal mucosa was measured 4 h after infection, allowing us to correlate enterotoxin secretion with gene regulation. Microarray analysis showed on the one hand a non-toxin related general antibacterial response comprising genes such as PAP, MMP1 and IL8. On the other hand, results suggest a dominant role for STb in small intestinal secretion early after post-weaning infection, as well as in the induced innate immune response through differential regulation of immune mediators like interleukin 1 and interleukin 17.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Porcine Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Strains Differ in Their Capacity To Secrete Enterotoxins through Varying YghG Levels.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2020 Nov 24;86(24):e00523-20. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00523-20. Print 2020 Nov 24. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32561576 Free PMC article.
-
Inverse relationship between heat stable enterotoxin-b induced fluid accumulation and adherence of F4ac-positive enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in ligated jejunal loops of F4ab/ac fimbria receptor-positive swine.Vet Microbiol. 2013 Jan 25;161(3-4):315-24. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2012.07.048. Epub 2012 Aug 3. Vet Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 22901529
-
Avirulent K88 (F4)+ Escherichia coli strains constructed to express modified enterotoxins protect young piglets from challenge with a virulent enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strain that expresses the same adhesion and enterotoxins.Vet Microbiol. 2012 Oct 12;159(3-4):337-42. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2012.03.046. Epub 2012 Apr 6. Vet Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22541162
-
Enterotoxins, colonization factors and serotypes of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli from humans and animals.Microbiologia. 1991 Sep;7(2):57-73. Microbiologia. 1991. PMID: 1684712 Review.
-
Heat-Stable Enterotoxins of Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and Their Impact on Host Immunity.Toxins (Basel). 2019 Jan 8;11(1):24. doi: 10.3390/toxins11010024. Toxins (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30626031 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dietary butyrate and valerate glycerides impact diarrhea severity and immune response of weaned piglets under ETEC F4-ETEC F18 coinfection conditions.J Anim Sci. 2023 Jan 3;101:skad401. doi: 10.1093/jas/skad401. J Anim Sci. 2023. PMID: 38044688 Free PMC article.
-
Intestinal Epithelial Cells Modulate the Production of Enterotoxins by Porcine Enterotoxigenic E. coli Strains.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jun 13;23(12):6589. doi: 10.3390/ijms23126589. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35743033 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analysis of circular RNAs in porcine small intestine epithelial cells associated with susceptibility to Escherichia coli F4ac diarrhea.BMC Genomics. 2023 Apr 22;24(1):211. doi: 10.1186/s12864-022-08994-8. BMC Genomics. 2023. PMID: 37085748 Free PMC article.
-
Intestinal Microbiota-Derived GABA Mediates Interleukin-17 Expression during Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli Infection.Front Immunol. 2017 Jan 16;7:685. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00685. eCollection 2016. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28138329 Free PMC article.
-
Dihydromyricetin alleviates ETEC K88-induced intestinal inflammatory injury by inhibiting quorum sensing-related virulence factors.BMC Microbiol. 2025 Apr 9;25(1):201. doi: 10.1186/s12866-025-03879-8. BMC Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40205366 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nagy B, Fekete PZ. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in veterinary medicine. Int J Med Microbiol. 2005;295:443–454. - PubMed
-
- Guerrant RL, Oria R, Bushen OY, Patrick PD, Houpt E, et al. Global impact of diarrheal diseases that are sampled by travelers: the rest of the hippopotamus. Clin Infect Dis. 2005;41:S524–530. - PubMed
-
- Thapar N, Sanderson IR. Diarrhoea in children: an interface between developing and developed countries. Lancet. 2004;363:641–653. - PubMed
-
- van der Meulen J, Hulst MM, Smits MA, Schuurman T. Small intestinal segment perfusion test in piglets: future applications in studying probiotics-gut crosstalk in infectious diarrhoea? Benef Microbes. 2010;1:439–445. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

