Vitamin E isoforms differentially regulate intercellular adhesion molecule-1 activation of PKCα in human microvascular endothelial cells
- PMID: 22815910
- PMCID: PMC3398863
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0041054
Vitamin E isoforms differentially regulate intercellular adhesion molecule-1 activation of PKCα in human microvascular endothelial cells
Abstract
Aims: ICAM-1-dependent leukocyte recruitment in vivo is inhibited by the vitamin E isoform d-α-tocopherol and elevated by d-γ-tocopherol. ICAM-1 is reported to activate endothelial cell signals including protein kinase C (PKC), but the PKC isoform and the mechanism for ICAM-1 activation of PKC are not known. It is also not known whether ICAM-1 signaling in endothelial cells is regulated by tocopherol isoforms. We hypothesized that d-α-tocopherol and d-γ-tocopherol differentially regulate ICAM-1 activation of endothelial cell PKC.
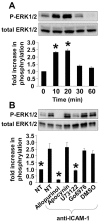
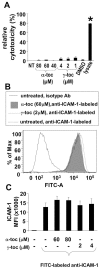
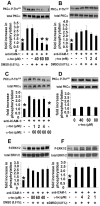
Results: ICAM-1 crosslinking activated the PKC isoform PKCα but not PKCβ in TNFα-pretreated human microvascular endothelial cells. ICAM-1 activation of PKCα was blocked by the PLC inhibitor U73122, ERK1/2 inhibitor PD98059, and xanthine oxidase inhibitor allopurinol. ERK1/2 activation was blocked by inhibition of XO and PLC but not by inhibition of PKCα, indicating that ERK1/2 is downstream of XO and upstream of PKCα during ICAM-1 signaling. During ICAM-1 activation of PKCα, the XO-generated ROS did not oxidize PKCα. Interestingly, d-α-tocopherol inhibited ICAM-1 activation of PKCα but not the upstream signal ERK1/2. The d-α-tocopherol inhibition of PKCα was ablated by the addition of d-γ-tocopherol.
Conclusions: Crosslinking ICAM-1 stimulated XO/ROS which activated ERK1/2 that then activated PKCα. ICAM-1 activation of PKCα was inhibited by d-α-tocopherol and this inhibition was ablated by the addition of d-γ-tocopherol. These tocopherols regulated ICAM-1 activation of PKCα without altering the upstream signal ERK1/2. Thus, we identified a mechanism for ICAM-1 activation of PKC and determined that d-α-tocopherol and d-γ-tocopherol have opposing regulatory functions for ICAM-1-activated PKCα in endothelial cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Broide DH, Humber D, Sullivan S, Sriramarao P. Inhibition of eosinophil rolling and recruitment in P-selectin- and intracellular adhesion molecule-1-deficient mice. Blood. 1998;91:2847–2856. - PubMed
-
- Chin JE, Hatfield CA, Winterrowd GE, Brashler JR, Vonderfecht SL, et al. Airway recruitment of leukocytes in mice is dependent on alpha4-integrins and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1. Am J Physiol. 1997;272:L219–L229. - PubMed
-
- Wolyniec WW, De SGT, Nabozny G, Torcellini C, Haynes N, et al. Reduction of antigen-induced airway hyperreactivity and eosinophilia in ICAM-1-deficient mice. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1998;18:777–785. - PubMed
-
- Kaminuma O, Fujimura H, Fushimi K, Nakata A, Sakai A, et al. Dynamics of antigen-specific helper T cells at the initiation of airway eosinophilic inflammation. Eur J Immunol. 2001;31:2669–2679. - PubMed
-
- Laberge S, Rabb H, Issekutz TB, Martin JG. Role of VLA-4 and LFA-1 in allergen-induced airway hyperresponsiveness and lung inflammation in the rat. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1995;151:822–829. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

