The effect of a pre- and post-operative orthogeriatric service on cognitive function in patients with hip fracture. The protocol of the Oslo Orthogeriatrics Trial
- PMID: 22817102
- PMCID: PMC3583172
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2318-12-36
The effect of a pre- and post-operative orthogeriatric service on cognitive function in patients with hip fracture. The protocol of the Oslo Orthogeriatrics Trial
Abstract
Background: Hip fractures mainly affect older people. It is associated with high morbidity and mortality, and in particular a high frequency of delirium. Incident delirium following hip fracture is associated with an increased risk of dementia in the following months, but it is still not firmly established whether this is an association or a causal relationship. Orthogeriatric units vary with respect to content and timing of the intervention. One main effect of orthogeriatric care may be the prevention of delirium, especially if preoperative and postoperative care are provided. Thus, the aim of Oslo Orthogeriatric Trial, is to assess whether combined preoperative and postoperative orthogeriatric care can reduce the incidence of delirium and improve cognition following hip fracture.
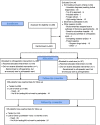
Methods/design: Inclusion and randomisation will take place in the Emergency Department, as soon as possible after admission. All patients with proximal femur fractures are eligible, irrespective of age, pre-fracture function and accommodation, except if the fracture is caused by a high energy trauma or the patient is terminally ill. The intervention is pre-and post-operative orthogeriatric care delivered on a dedicated acute geriatric ward. The primary outcome measure is a composite endpoint combining the Clinical Dementia Rating Scale (CDR) and the 10 word memory task at four months after surgery. Secondary outcomes comprise incident delirium, length of stay, cognition, mobility, place of residence, activities of daily living and mortality, measured at 4 and 12 months after surgery. We have included 332 patients in the period 17th September 2009 to 5th January 2012.
Discussion: Our choice of outcome measures and our emphasis of orthogeriatric care in the preoperative as well as the postoperative phase will enable us to provide new knowledge on the impact of orthogeriatric care on cognition.
Trials registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01009268.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical