An analog of the natural steroidal alkaloid cortistatin A potently suppresses Tat-dependent HIV transcription
- PMID: 22817991
- PMCID: PMC3403716
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chom.2012.05.016
An analog of the natural steroidal alkaloid cortistatin A potently suppresses Tat-dependent HIV transcription
Abstract
The human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV) Tat protein, a potent activator of HIV gene expression, is essential for integrated viral genome expression and represents a potential antiviral target. Tat binds the 5'-terminal region of HIV mRNA's stem-bulge-loop structure, the transactivation-responsive (TAR) element, to activate transcription. We find that didehydro-Cortistatin A (dCA), an analog of a natural steroidal alkaloid from a marine sponge, inhibits Tat-mediated transactivation of the integrated provirus by binding specifically to the TAR-binding domain of Tat. Working at subnanomolar concentrations, dCA reduces Tat-mediated transcriptional initiation/elongation from the viral promoter to inhibit HIV-1 and HIV-2 replication in acutely and chronically infected cells. Importantly, dCA abrogates spontaneous viral particle release from CD4(+)T cells from virally suppressed subjects on highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART). Thus, dCA defines a unique class of anti-HIV drugs that may inhibit viral production from stable reservoirs and reduce residual viremia during HAART.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
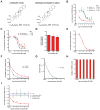

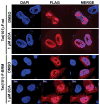
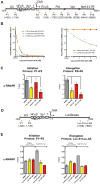


Comment in
-
An Ounce of Tat Prevention Is Worth a Pound of Functional Cure.mBio. 2015 Aug 18;6(4):e01269-15. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01269-15. mBio. 2015. PMID: 26286696 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Alcami J, Lain de Lera T, Folgueira L, Pedraza MA, Jacque JM, Bachelerie F, Noriega AR, Hay RT, Harrich D, Gaynor RB, et al. Absolute dependence on kappa B responsive elements for initiation and Tat-mediated amplification of HIV transcription in blood CD4 T lymphocytes. Embo J. 1995;14:1552–1560. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aoki S, Watanabe Y, Sanagawa M, Setiawan A, Kotoku N, Kobayashi M. Cortistatins A, B, C, and D, anti-angiogenic steroidal alkaloids, from the marine sponge Corticium simplex. J Am Chem Soc. 2006;128:3148–3149. - PubMed
-
- Aoki S, Watanabe Y, Tanabe D, Arai M, Suna H, Miyamoto K, Tsujibo H, Tsujikawa K, Yamamoto H, Kobayashi M. Structure-activity relationship and biological property of cortistatins, anti-angiogenic spongean steroidal alkaloids. Bioorg Med Chem. 2007;15:6758–6762. - PubMed
-
- Arima N, Kuziel WA, Grdina TA, Greene WC. IL-2-induced signal transduction involves the activation of nuclear NF-kappa B expression. J Immunol. 1992;149:83–91. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

