Jakinibs: a new class of kinase inhibitors in cancer and autoimmune disease
- PMID: 22819198
- PMCID: PMC3419278
- DOI: 10.1016/j.coph.2012.06.008
Jakinibs: a new class of kinase inhibitors in cancer and autoimmune disease
Abstract
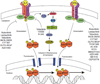
Cytokines are critical for normal cell growth and immunoregulation but also contribute to growth of malignant cells and drive immune-mediated disease. A large subset of immunoregulatory cytokines uses the type I and type II cytokine receptors and pharmacological targeting of these cytokines/cytokines receptors has proven to be efficacious in treating immune and inflammatory diseases. These receptors rely on Janus family of kinases (Jaks) for signal transduction. Recently the first Jak inhibitor (jakinib) has been approved by the FDA and a second has been recommended for approval. Many other Jakinibs are likely to follow and in this brief review, we will discuss the state-of-the art of this new class of pharmacological agents.
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures
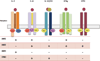
References
-
- Boulay JL, O'Shea JJ, Paul WE. Molecular phylogeny within type I cytokines and their cognate receptors. Immunity. 2003;19(2):159–163. - PubMed
-
- Leonard WJ, O'Shea JJ. Jaks and STATs: biological implications. Annu Rev Immunol. 1998;16:293–322. - PubMed
-
- Darnell JE, Jr, Kerr IM, Stark GR. Jak-STAT pathways and transcriptional activation in response to IFNs and other extracellular signaling proteins. Science. 1994;264(5164):1415–1421. - PubMed
-
- Levy DE, Darnell JE., Jr Stats: transcriptional control and biological impact. Nature reviews. Molecular cell biology. 2002;3(9):651–662. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

