Early life manipulations alter learning and memory in rats
- PMID: 22819985
- PMCID: PMC3463710
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2012.07.003
Early life manipulations alter learning and memory in rats
Abstract
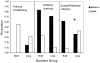
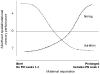
Much research shows that early life manipulations have enduring behavioral, neural, and hormonal effects. However, findings of learning and memory performance vary widely across studies. We reviewed studies in which pre-weaning rat pups were exposed to stressors and tested on learning and memory tasks in adulthood. Tasks were classified as aversive conditioning, inhibitory learning, or spatial/relational memory. Variables of duration, type, and timing of neonatal manipulation and sex and strain of animals were examined to determine if any predict enhanced or impaired performance. Brief separations enhanced and prolonged separations impaired performance on spatial/relational tasks. Performance was impaired in aversive conditioning and enhanced in inhibitory learning tasks regardless of manipulation duration. Opposing effects on performance for spatial/relational memory also depended upon timing of manipulation. Enhanced performance was likely if the manipulation occurred during postnatal week 3 but performance was impaired if it was confined to the first two postnatal weeks. Thus, the relationship between early life experiences and adulthood learning and memory performance is multifaceted and decidedly task-dependent.
Copyright © 2012 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Abraham IM, Kovacs KJ. Postnatal handling alters the activation of stress-related neuronal circuitries. European Journal of Neuroscience. 2000;12:3003–3014. - PubMed
-
- Ader R. Effects of early experiences on shock- and illness-induced passive avoidance behaviors. Developmental Psychobiology. 1973;6:547–555. - PubMed
-
- Ader R, Grota LJ. Effects of early experience on adrenocortical reactivity. Physiology & Behavior. 1969;4:303–305.
-
- Aisa B, Elizalde N, Tordera R, Lasheras B, DelRio J, Ramirez MJ. Effects of neonatal stress on markers of synaptic plasticity in the hippocampus: implications for spatial memory. Hippocampus. 2009a;19:1222–1231. - PubMed
-
- Aisa B, Gil-Bea FJ, Marcos B, Tordera R, Lasheras B, DelRio J, Ramirez MJ. Neonatal stress affects vulnerability of cholinergic neurons and cognition in the rat: Involvment of the HPA axis. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2009b;34:1495–1505. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

