Essential metabolic, anti-inflammatory, and anti-tumorigenic functions of miR-122 in liver
- PMID: 22820288
- PMCID: PMC3408748
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI63539
Essential metabolic, anti-inflammatory, and anti-tumorigenic functions of miR-122 in liver
Abstract
miR-122, an abundant liver-specific microRNA (miRNA), regulates cholesterol metabolism and promotes hepatitis C virus (HCV) replication. Reduced miR-122 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) correlates with metastasis and poor prognosis. Nevertheless, the consequences of sustained loss of function of miR-122 in vivo have not been determined. Here, we demonstrate that deletion of mouse Mir122 resulted in hepatosteatosis, hepatitis, and the development of tumors resembling HCC. These pathologic manifestations were associated with hyperactivity of oncogenic pathways and hepatic infiltration of inflammatory cells that produce pro-tumorigenic cytokines, including IL-6 and TNF. Moreover, delivery of miR-122 to a MYC-driven mouse model of HCC strongly inhibited tumorigenesis, further supporting the tumor suppressor activity of this miRNA. These findings reveal critical functions for miR-122 in the maintenance of liver homeostasis and have important therapeutic implications, including the potential utility of miR-122 delivery for selected patients with HCC and the need for careful monitoring of patients receiving miR-122 inhibition therapy for HCV.
Figures
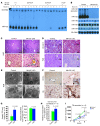
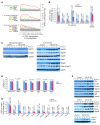
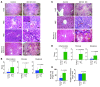

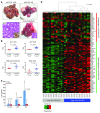
Comment in
-
miR-122 acts as a tumor suppressor in hepatocarcinogenesis in vivo.J Hepatol. 2013 Apr;58(4):821-3. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2012.10.010. Epub 2012 Oct 17. J Hepatol. 2013. PMID: 23085250 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

